Filtration Anatomy
Causes vasodilation in kidney afferent arteriole and causes vasoconstriction in efferent arteriole. One of the main functions of the kidneys is to filter various substances out of the blood such as salts electrolytes and waste products.
Filtration diffusion and osmosis introduction the processes of diffusion osmosis and filtration are responsible for the movement of materials into and out of body cells as well as the exchange of molecules between body fluid compartments.

Filtration anatomy. The kidney requires sym does high levels of adh in the blood ca if you primarily wanted to alter blood if you primarily wanted to alter glomer the kidney is capable of autoregulation and normal fun high levels of adh will cause both gfr and rpf to decrease. However if you increase the pressure on one side of the membrane of the fluid as a whole you force more water through the membrane. This is where the mixture is poured from a higher point to a lower one.
Accounts for 2 of kidney failures each year. Mechanism for the maintenance of renal blood flow and glomerular blood flow hormonal regulation. Solutes include glucose gases ions hormones and vitamins anything dissolved in the plasma of the blood that is small enough to pass through the pores in.
In radiology process of attenuating and hardening a beam of x or gamma rays by interposing a filter between radiation source and the object being irradiated. In vacuum filtration a vacuum pump is used to rapidly draw. Types of filtration vacuum filtration.
This kind of filtration is done by rotating the substance to be filtered. The goal is to get rid of excess fluid. Concentration gradient is high to low.
Reabsorption involves the absorption of molecules ions and water that are necessary for the body to maintain homeostasis from the glomerular filtrate back into the blood. Filtration involves the transfer of soluble components such as water and waste from the blood into the glomerulus. An inherited disorder characterized by many grape like clusters of fluid filled cysts that make both kidneys larger over time taking over and destroying working kidney tissue.
These processes involve some basic principles of physics which will be demonstrated in this laboratory. Urinary system anatomy and filtration. If enough pressure is applied to the side with the solute then it can overcome the pressure differences across the pores and reverse them causing water to flow against its concentration gradient.
Water and solutes are forced through pores of a body membrane by the hydrostatic pressure of blood ie. What is filtration in anatomy. Process of passing liquid or gas through a filter.
Increases renal blood flow and increases glomerular filtration rate.

 Figure 1 From Glomerular Filtration An Overview Semantic
Figure 1 From Glomerular Filtration An Overview Semantic
 Imaging 2 Unit 1 Density Contrast Detail Distortion
Imaging 2 Unit 1 Density Contrast Detail Distortion
 Waste Filtration Kidney Stock Image C043 7000 Science
Waste Filtration Kidney Stock Image C043 7000 Science
 Anatomy And Cell Biology 3309 Lecture 11 33 Oneclass
Anatomy And Cell Biology 3309 Lecture 11 33 Oneclass
 Anatomy Of A Pharmaceutical Filtration Differential
Anatomy Of A Pharmaceutical Filtration Differential
 058 Net Hydrostatic Pressure And Filtration Pressure
058 Net Hydrostatic Pressure And Filtration Pressure
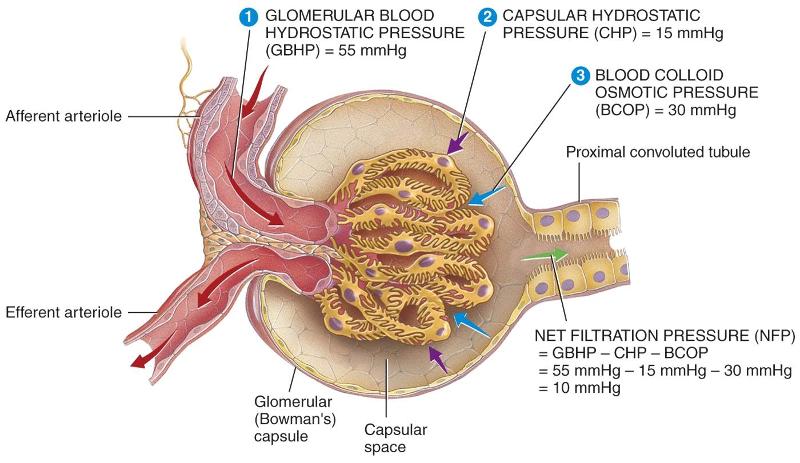 4 Urinary System Glomerular Filtration Flashcards Easy
4 Urinary System Glomerular Filtration Flashcards Easy
 Glomerular Filtration And Regulation Of Glomerular
Glomerular Filtration And Regulation Of Glomerular
 Filtration Membrane Blood Components Blood Plasma Physiology
Filtration Membrane Blood Components Blood Plasma Physiology
Anatomy 124 My Lecture Notes From December 4 Bios 2110
 The First Step The Kidney Takes To Convert Blood Plasma To
The First Step The Kidney Takes To Convert Blood Plasma To
 2 Glomerular Anatomy And Physiology At Utah Valley
2 Glomerular Anatomy And Physiology At Utah Valley
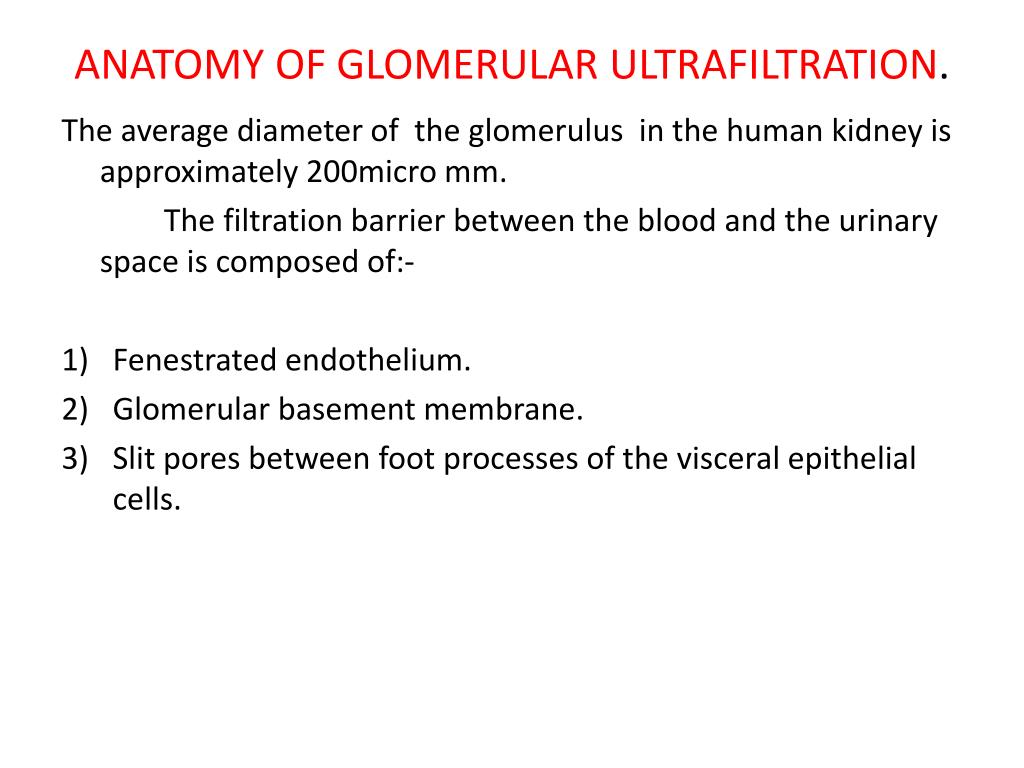 Ppt Glomerular Ultrafiltration Anatomy And Physiology
Ppt Glomerular Ultrafiltration Anatomy And Physiology
 Ppt Urinary System Renal Function Powerpoint Presentation
Ppt Urinary System Renal Function Powerpoint Presentation
 Anatomy Semester Exam Study Guide
Anatomy Semester Exam Study Guide
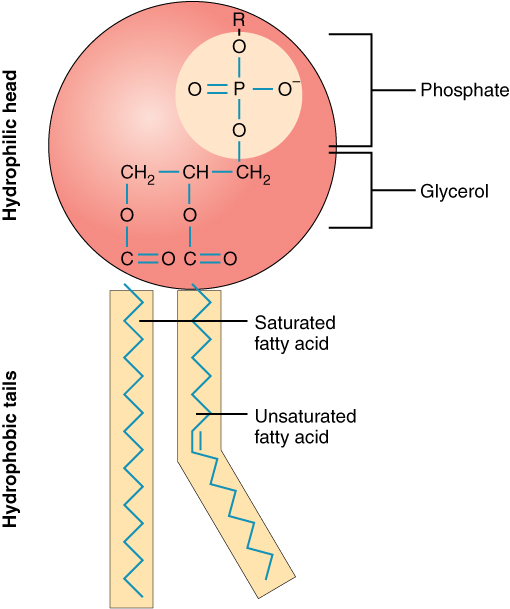 3 1 The Cell Membrane Anatomy And Physiology
3 1 The Cell Membrane Anatomy And Physiology
 Kidney Filtration Madeline M Lee
Kidney Filtration Madeline M Lee
 Assessment Of Glomerular Filtration Rate In Older Adults In
Assessment Of Glomerular Filtration Rate In Older Adults In

 Glomerular Filtration Rate Gfr Renal Medbullets Step 2 3
Glomerular Filtration Rate Gfr Renal Medbullets Step 2 3









Belum ada Komentar untuk "Filtration Anatomy"
Posting Komentar