Ear And Jaw Anatomy
You will discover four primary jaw muscles on your tmj anatomy tour. It is important to see a doctor even though you may identify the cause of your jaw and ear pain yourself.
Learn about the ears function in the body and test and.

Ear and jaw anatomy. Tmj disorders affect the temporomandibular joint located on each side of your head in front of your ears. In regards to jaw anatomy the major joint in the jaw is the temporomandibular joint tmj which connects the lower jaw to the skull temporal bone under the ear. Unless you have teeth alignment or existing jaw bone problems experiencing pain in the area between your jaw and you ear is a sign of mandibular tension and possibly inflammation called temporomandibular pain it involves the temporal and mandible areas.
Ear and jaw pain can sometimes occur because pain from one area is felt in another part of the head or face. The temporomandibular tem puh roe man dib u lur joint tmj acts like a sliding hinge connecting your jawbone to your skull. Well come to the fourth muscle in due course.
A soft cartilage disk acts as a cushion between the bones of the joint so the joint can move smoothly. Some physicians associate disorder in this joint with tiny myofascial trigger points or contractions knots in the overworked or traumatized jaw muscles. Tmj or something else with the jaw apparatus.
Helpful trusted answers from doctors. This joint also known as the tmj connects your jaw to the rest of your skull and allows you to push your jaw back forward and sideways and open. They open close protrude and move the jaw sideways enabling you to talk chew and swallow kiss and many other things we do with our mouths.
From fossil data comparative anatomy and developmental biology it is now clear that the two new bones in the mammalian middle ear the malleus and incus are homologous to the quadrate and articular which form the articulation for the upper and lower jaws in non mammalian jawed vertebrates. Webmds ear anatomy page provides a detailed image and definition of the ear as well as an overview of ear related health problems. The oto mandibular ligaments are the discomalleolar ligament dml which arises from the malleus one of the ossicles of the middle ear and runs to the medial retrodiscal tissue of the tmj and the anterior malleolar ligament aml which arises from the malleus and connects with the lingula of the mandible via the sphenomandibular ligament.
People open their mouths to chew speak and swallow without a second thought thanks to the bodys complex and unique temporomandibular joint anatomy. Conditions such as tmj and ear infections may cause pain in both areas. Southard on anatomy of the jaw and ear.
See an oral surgeon for examination. There are three kinds of tmj anatomy pain.
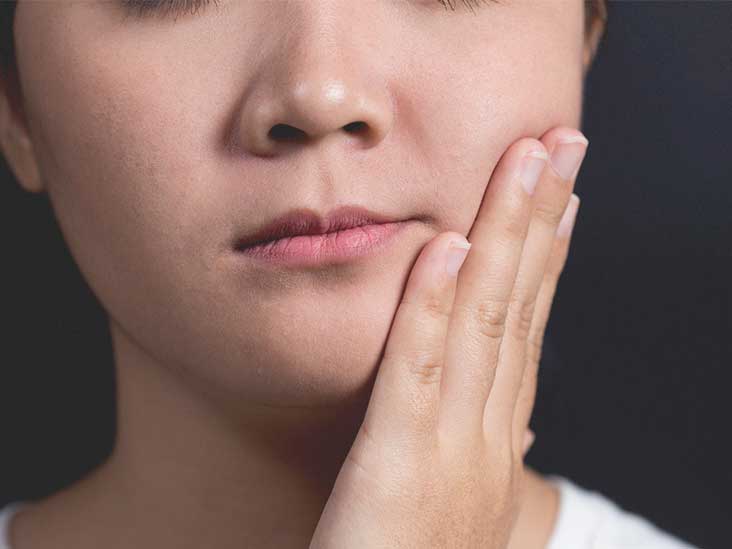 Ear And Jaw Pain 8 Causes Symptoms And Treatments
Ear And Jaw Pain 8 Causes Symptoms And Treatments
 Mandibular Nerve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Mandibular Nerve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Tmj Tmd Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Arizona Tmj
 Stubborn Tmj Pain Try Trigger Point Massage And Jaw
Stubborn Tmj Pain Try Trigger Point Massage And Jaw
 5 Times Life Size Giant Ear Anatomy Model 3 Parts
5 Times Life Size Giant Ear Anatomy Model 3 Parts
 Tmj Jaw Pain Symptoms Signs Treatment Causes Home
Tmj Jaw Pain Symptoms Signs Treatment Causes Home
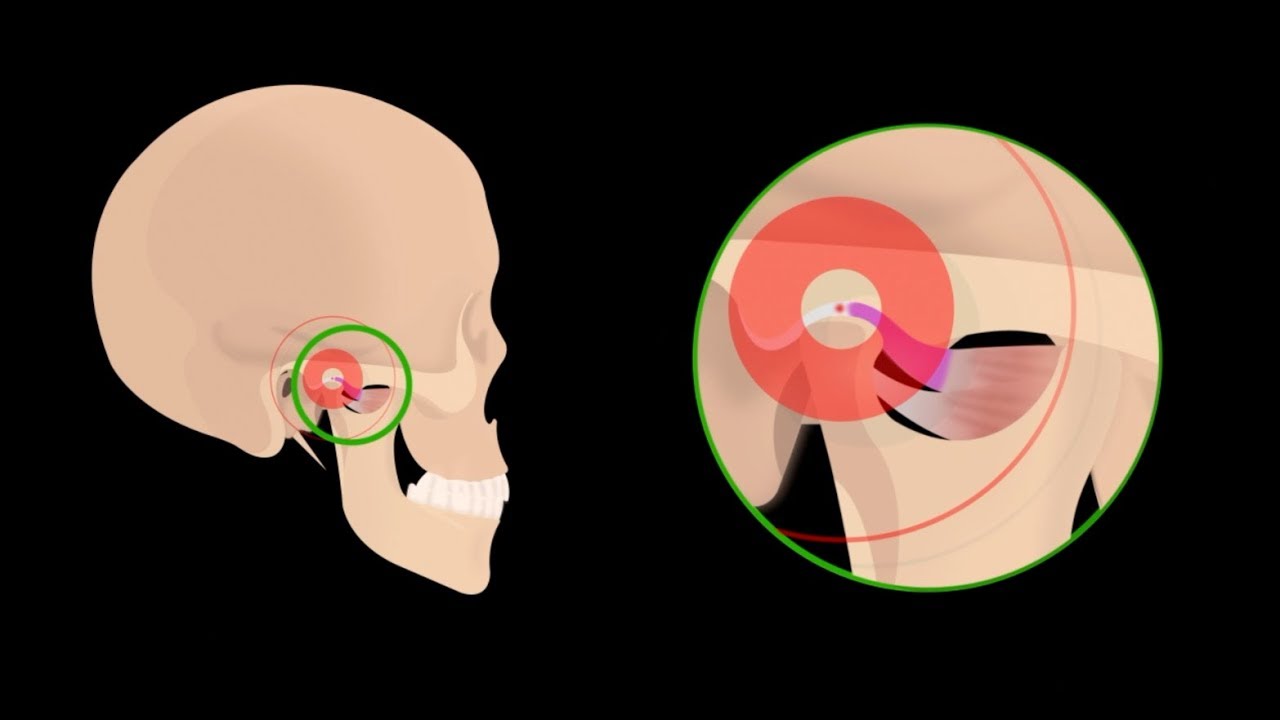 Ear Pain Due To Tmj Jaw Joint Disorders
Ear Pain Due To Tmj Jaw Joint Disorders
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-causes-a-retracted-ear-drum-1191976-5c04ac1e46e0fb0001dd5eba.png) Retracted Ear Drum Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Retracted Ear Drum Causes Symptoms And Treatment
![]() 13 Treatments For Clenching Or Grinding Related Headache
13 Treatments For Clenching Or Grinding Related Headache
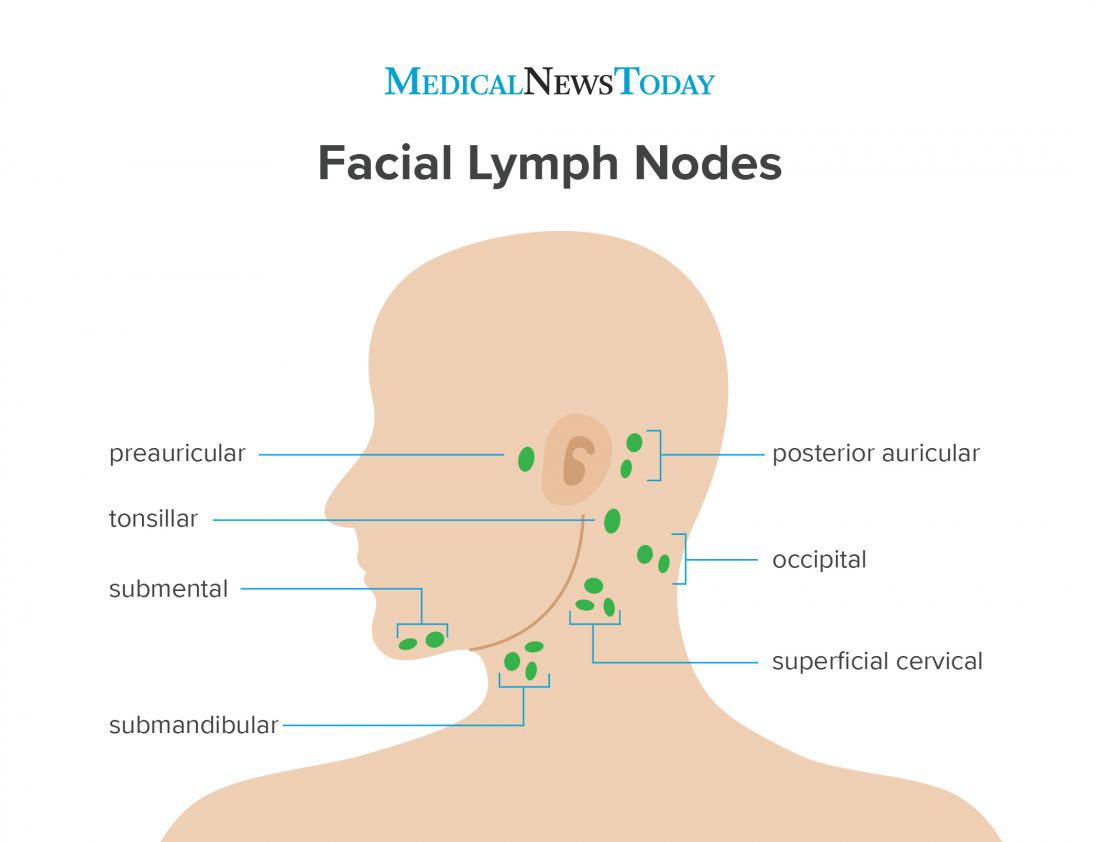 Preauricular Lymph Nodes Causes Of Swelling
Preauricular Lymph Nodes Causes Of Swelling
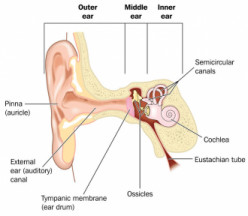 Earwax Build Up And Removal Health Navigator Nz
Earwax Build Up And Removal Health Navigator Nz
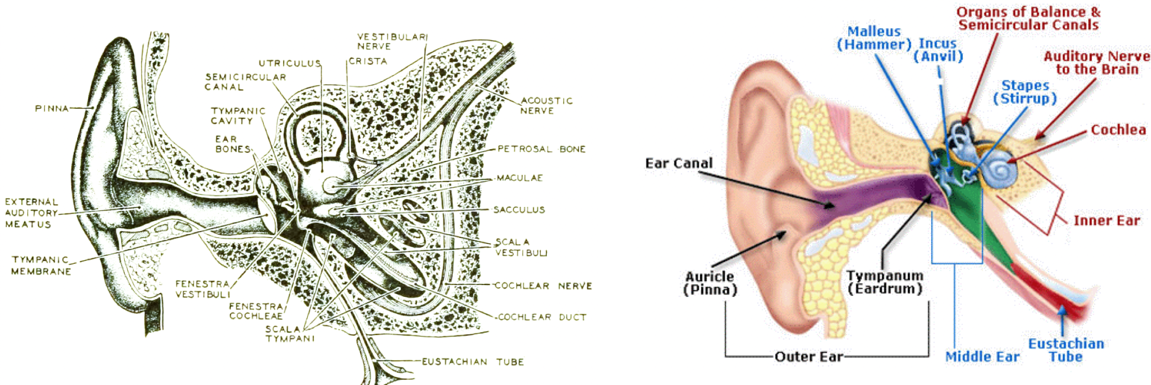 The Moovin Groovin Outer Ear Lydia Gregoret Hearing Aids
The Moovin Groovin Outer Ear Lydia Gregoret Hearing Aids
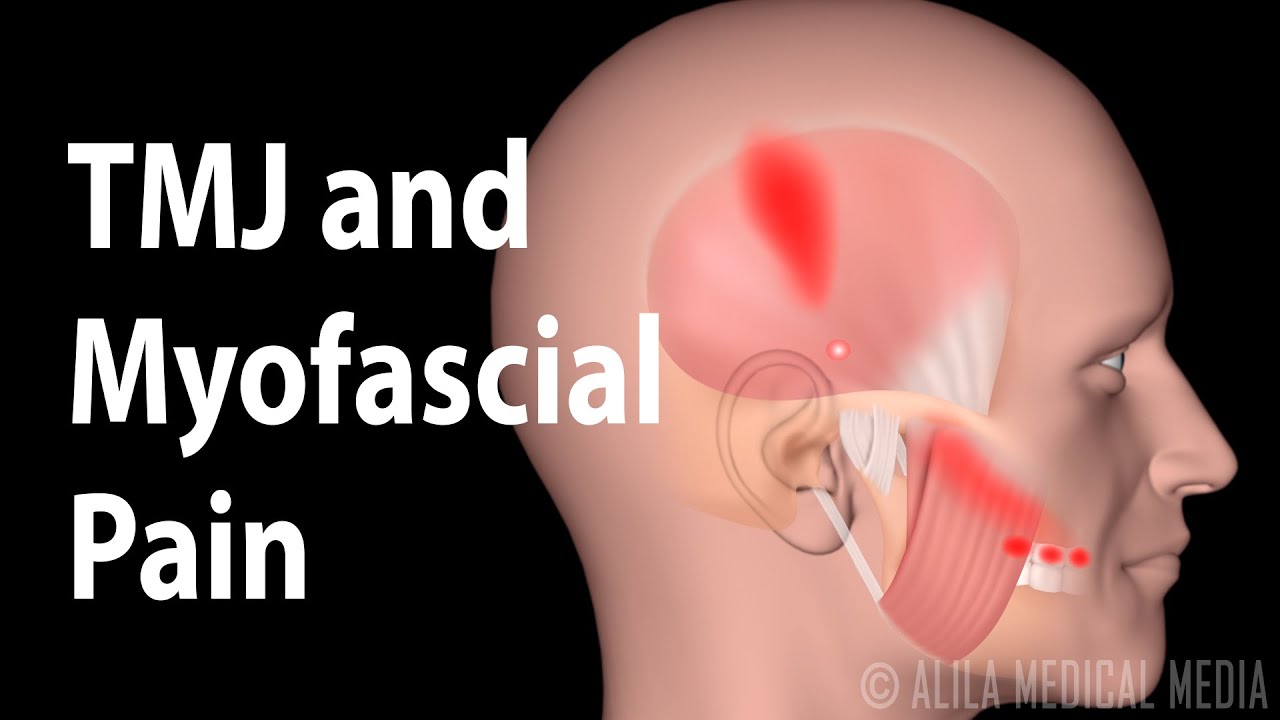 Tmj And Myofascial Pain Syndrome Animation
Tmj And Myofascial Pain Syndrome Animation
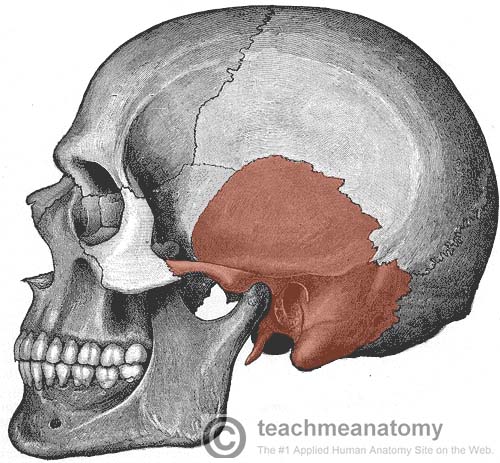 The Temporal Bone Parts Fractures Teachmeanatomy
The Temporal Bone Parts Fractures Teachmeanatomy
 How To Treat Tmj Syndrome Symptoms Causes Treatment
How To Treat Tmj Syndrome Symptoms Causes Treatment
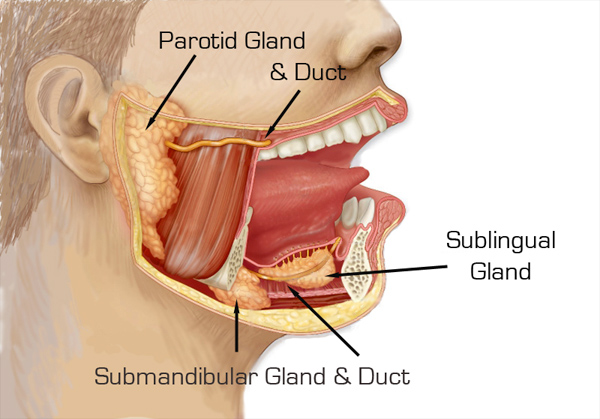 Anatomy Of The Parotid Submandibular Glands Ducts Dr
Anatomy Of The Parotid Submandibular Glands Ducts Dr
 Inner Ear Anatomy Function And Health
Inner Ear Anatomy Function And Health
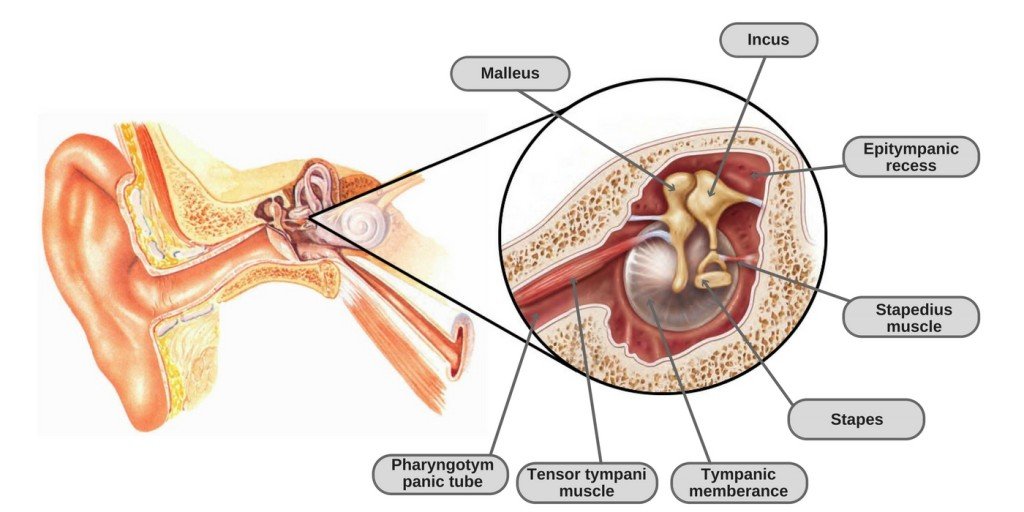 Tensor Tympani Why Closing The Eyes Tightly Causes
Tensor Tympani Why Closing The Eyes Tightly Causes
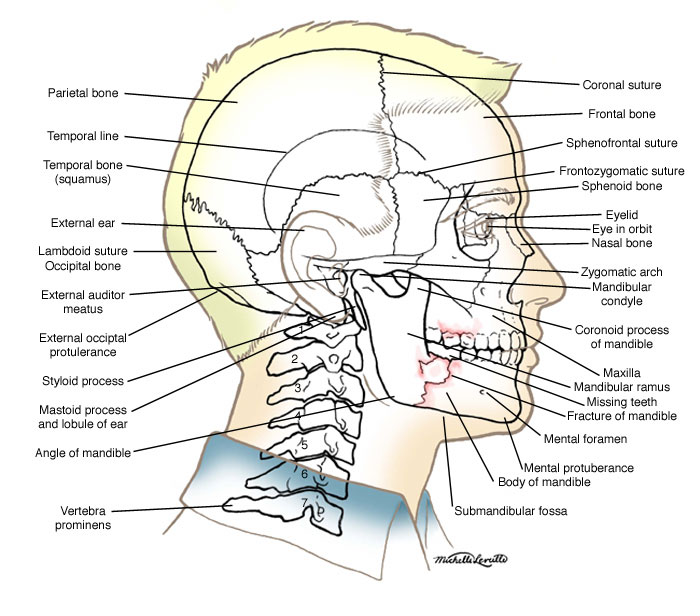 Anatomy Atlases Anatomy Of First Aid A Case Study Approach
Anatomy Atlases Anatomy Of First Aid A Case Study Approach
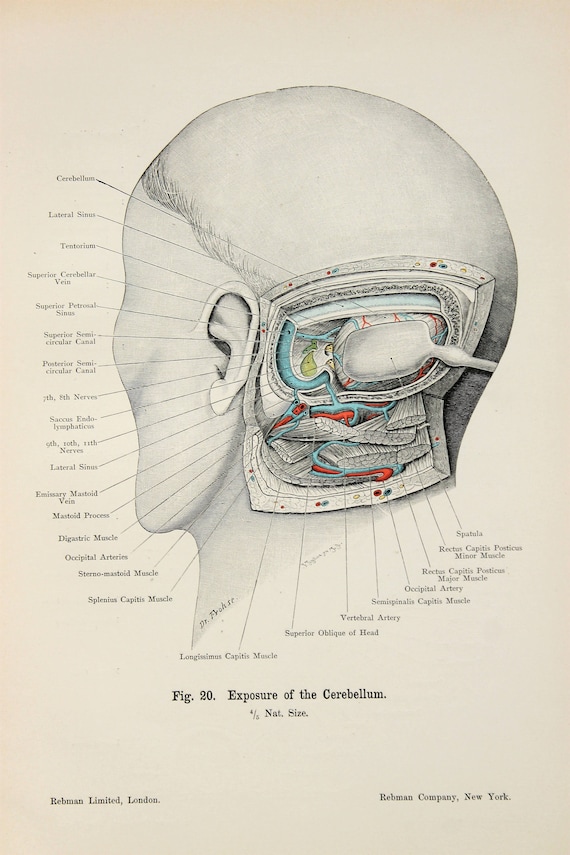 Skull Anatomy Cerebellum Ears Hearing C 1900 Double Sided Antique Anatomy Print Colour Anatomical Print Lithograph
Skull Anatomy Cerebellum Ears Hearing C 1900 Double Sided Antique Anatomy Print Colour Anatomical Print Lithograph
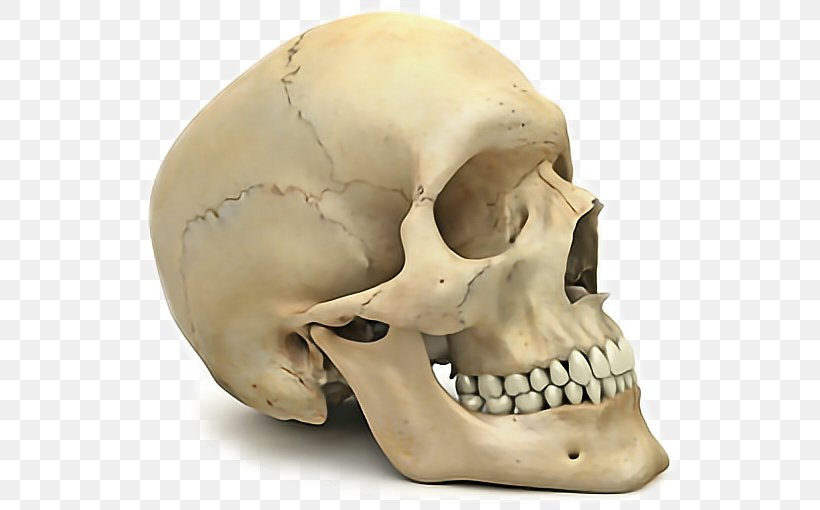 Skull Anatomy Png 544x510px Skull Anatomy Bone Chin
Skull Anatomy Png 544x510px Skull Anatomy Bone Chin
 Nerve Blocks Of The Face Nysora
Nerve Blocks Of The Face Nysora
 Amazon Com Anatomy Ear Jaw Vein Print Sra3 12x18 Conqueror
Amazon Com Anatomy Ear Jaw Vein Print Sra3 12x18 Conqueror




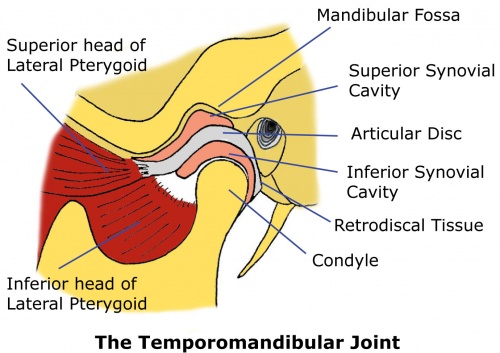
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Ear And Jaw Anatomy"
Posting Komentar