Anatomy Of Nematodes
Pseudocoelom body cavity fluid filled under pressure so that worm can move when muscles contract. General anatomy and physiology.
Round worms are also triploblastic.
Anatomy of nematodes. Identify and describe a variety of morphological and anatomical features used in nematode classification. Four out of every five multicellular animals on the planet are nematodes platt 1994. The hypodermis is an epidermis composed of a thin layer of cells.
The nematodes or roundworms constitute the phylum nematoda. Locomotion in nematodes involves somatic muscles that are. By the end of this course students will.
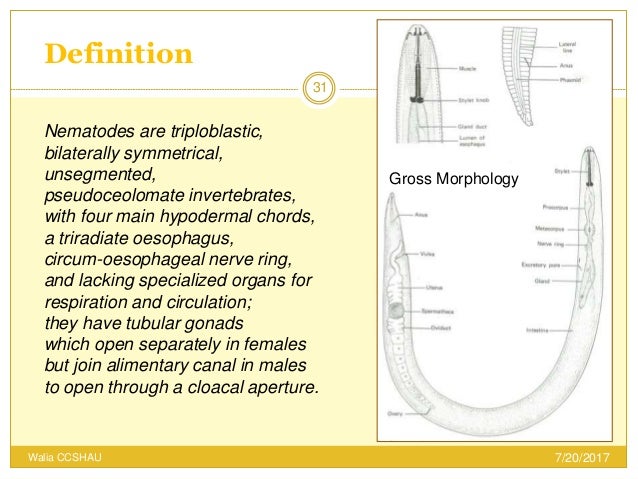
Several organ systems are present. Principles are common to all nematodes. Nematodes are triploblastic bilaterally symmetrical unsegmented pseudocoelomate vermiform and colourless animals.
Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Taxonomically they are classified along with insects and other moulting animals in the clade ecdysozoa and unlike flatworms have tubular digestive systems with openings at both ends. The head of a nematode has a few tiny sense organs and a mouth opening into a muscular pharynx throat where food is pulled in and crushed.
The structure of a nematode is intimately related to its function and its life cycle. A layer of muscles lies beneath the hypodermis layer and runs longitudinally along. Nematode structure and function overview.
This leads into a long simple gut cavity lacking any muscles and then to an anus near the tip of the body. A protective outer layer that is composed mainly of collagens that are cross linked. Taxonomically they are classified along with insects and other moulting animals in the clade ecdysozoa and unlike flatworms have tubular digestive systems with openings at both ends.
The nematodes or roundworms constitute the phylum nematoda. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. They comprise the phylum nematoda or nemata which includes parasites of plants and of animals including humans as well as species that feed on bacteria fungi algae and on other nematodes.
Consequently estimates of the number of nematode species described to date vary by author and may change rapidl. The length of the nematode may vary. Like tardigrades they have a reduced number of hox genes but as their sister phylum nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome hox genotype it shows that the reduction has o.
Objective define anatomical terms with regard to function. Target of many anthelmintic deworming drugs. They are the first animals to evolve a complete digestive tract with a mouth and anus.
Dorsal and ventral cords major nerves. Movement is essential for nematode survival. Nematodes are invertebrate roundworms that inhabit marine freshwater and terrestrial environments.
They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Morphology anatomy and physiology that informs about nematode feeding habits their taxonomic diversity and potential habitats and functioning. The plant parasitic nematodes are slender elongate spindle shaped or fusiform tapering towards both ends and circular in cross section.
The nematode body is cylindrical elongated and smooth with no limbs protruding. Course goals andor objectives. Nematodes are tapered at both ends.
 Evolution Of Pharyngeal Behaviors And Neuronal Functions In
Evolution Of Pharyngeal Behaviors And Neuronal Functions In
 Anatomy Of Model Intestinal Nematode Species Ascaris Suum
Anatomy Of Model Intestinal Nematode Species Ascaris Suum
 Nematode Nervous Systems Sciencedirect
Nematode Nervous Systems Sciencedirect
 Figure 36 From Nematodes And Their Relationships Semantic
Figure 36 From Nematodes And Their Relationships Semantic
 Topic Nematode Round Worms Online Presentation
Topic Nematode Round Worms Online Presentation
 A Transparent Window Into Biology A Primer On
A Transparent Window Into Biology A Primer On
 Nematoda Free Living And Parasitic Roundworms
Nematoda Free Living And Parasitic Roundworms
 Nematode Structure And Function Wikivet English
Nematode Structure And Function Wikivet English
 Phylum Nematoda And Other Pseudocoelomate Animals Chapter 9
Phylum Nematoda And Other Pseudocoelomate Animals Chapter 9
 A Text Book Of Agricultural Zoology Zoology Economic 60
A Text Book Of Agricultural Zoology Zoology Economic 60
 Nematodes Review Of Medical Microbiology And Immunology
Nematodes Review Of Medical Microbiology And Immunology
 Ecdyzoan Phyla Figure 12 01 Phylum Nematoda Round Worms
Ecdyzoan Phyla Figure 12 01 Phylum Nematoda Round Worms
 15 3 Flatworms Nematodes And Arthropods Biology Libretexts
15 3 Flatworms Nematodes And Arthropods Biology Libretexts
 Introduction To Plant Parasitic Nematodes
Introduction To Plant Parasitic Nematodes
 Nematode Nervous Systems Sciencedirect
Nematode Nervous Systems Sciencedirect
 Nematode Nervous Systems Sciencedirect
Nematode Nervous Systems Sciencedirect
 Introduction To Plant Parasitic Nematodes
Introduction To Plant Parasitic Nematodes
 Phylum Nematoda Phylum Nematoda Ppt Download
Phylum Nematoda Phylum Nematoda Ppt Download
 Nematodes Parasites Of Higher Plants Rev 10
Nematodes Parasites Of Higher Plants Rev 10
 15 3 Flatworms Nematodes And Arthropods Biology Libretexts
15 3 Flatworms Nematodes And Arthropods Biology Libretexts
 Nematodes Review Of Medical Microbiology And Immunology
Nematodes Review Of Medical Microbiology And Immunology
 Nematoda Nematodes Digestive System In Phylums
Nematoda Nematodes Digestive System In Phylums
 Nematodes Are Also Known As Roundworms And Live In The
Nematodes Are Also Known As Roundworms And Live In The
 Introduction To Plant Parasitic Nematodes
Introduction To Plant Parasitic Nematodes

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Nematodes"
Posting Komentar