Neuron Anatomy
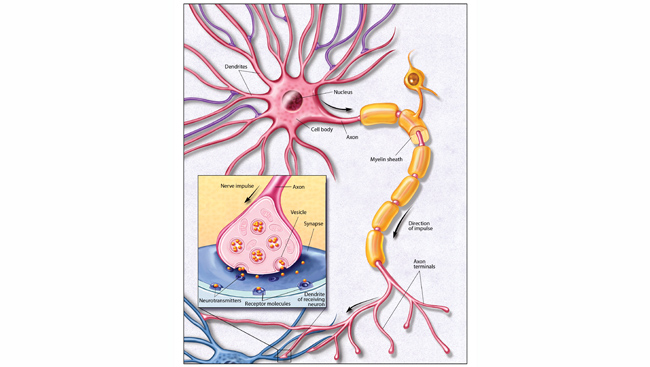
A typical neuron can be exemplified by a motor neuron in which the cell body of the nerve is located within the gray matter of the spinal cord and the nerve fibre or axon extends to the muscle. Impulses are carried along one or more of these fibres called dendrites.
 Sensory Neuron Anatomy Britannica
Sensory Neuron Anatomy Britannica
The basic functional units of nervous tissue and are highly specialized to transmit messages nerve impulses from one part of the body to another.

Neuron anatomy. A neuron also known as a neurone old british spelling or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell 1 that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. Neuron also called nerve cell basic cell of the nervous system in vertebrates and most invertebrates from the level of the cnidarians eg corals jellyfish upward. Schematic of an anatomically accurate single pyramidal neuron the primary excitatory neuron of cerebral cortex with a synaptic connection from an incoming axon onto a dendritic spine.
It could be a whole bunch of different things and well talk more about the different types of neurons. Nerve impulses are received at neuronal dendrites passed through the cell body and are carried along the axon to the terminal branches. Can receive input from sensory neurons and also from other inter neurons in the cns.
Mature neurons do not divide amitotic except for olfactoryepithelium and hippocampus. A typical neuron has a cell body containing a nucleus and two or more long fibres. Neurons or nerve cells are specialized cells that transmit and receive electrical signals in the body.
Lies entirely within the cns. They form the structural and functional unit of the nervous system and are responsible for all its activities. Nerve axons can be very long permitting electrical impulses to be sent over long distances throughout the body.
This could be on a taste bud someplace so a salt molecule somehow can trigger it or a sugar molecule or this might be some type of sensor. The excitable cells of the nervous system are known as neurons. The nervous tissue is composed of two distinct types of cells.
Myelin sheaths cover the axon and work like insulation to help keep the electrical signal inside the cell which makes it move more quickly. The excitable and the non excitable. This could be some type of sensory neuron.
These inter neurons sum up all the messages from these neurons before they communicate with the motor neurons. Next the signal leaves the soma and travels down the axon to the synapse. Nerve impulses or action potentials are electrochemical impulses that cause neurons to release electrical or chemical signals that initiate an action potential in another neuron.
From there the signal travels to the main cell body known as the soma. Neurons are composed of three main parts. A neuron that connects afferent and efferent neurons.
Dendrites a cell body and an axon.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/neuron-anatomy-58530ffe3df78ce2c34a7350.jpg) Neuron Anatomy Nerve Impulses And Classifications
Neuron Anatomy Nerve Impulses And Classifications
 Aab Neuron Anatomy Activity Pdf Document
Aab Neuron Anatomy Activity Pdf Document
 Cartoon Illustration Of Human Neuron Anatomy By Tigatelu
Cartoon Illustration Of Human Neuron Anatomy By Tigatelu
 Communication Between Neurons Anatomy And Physiology
Communication Between Neurons Anatomy And Physiology
 Lab Final Neuron Anatomy Exercise 13 Anatomy
Lab Final Neuron Anatomy Exercise 13 Anatomy
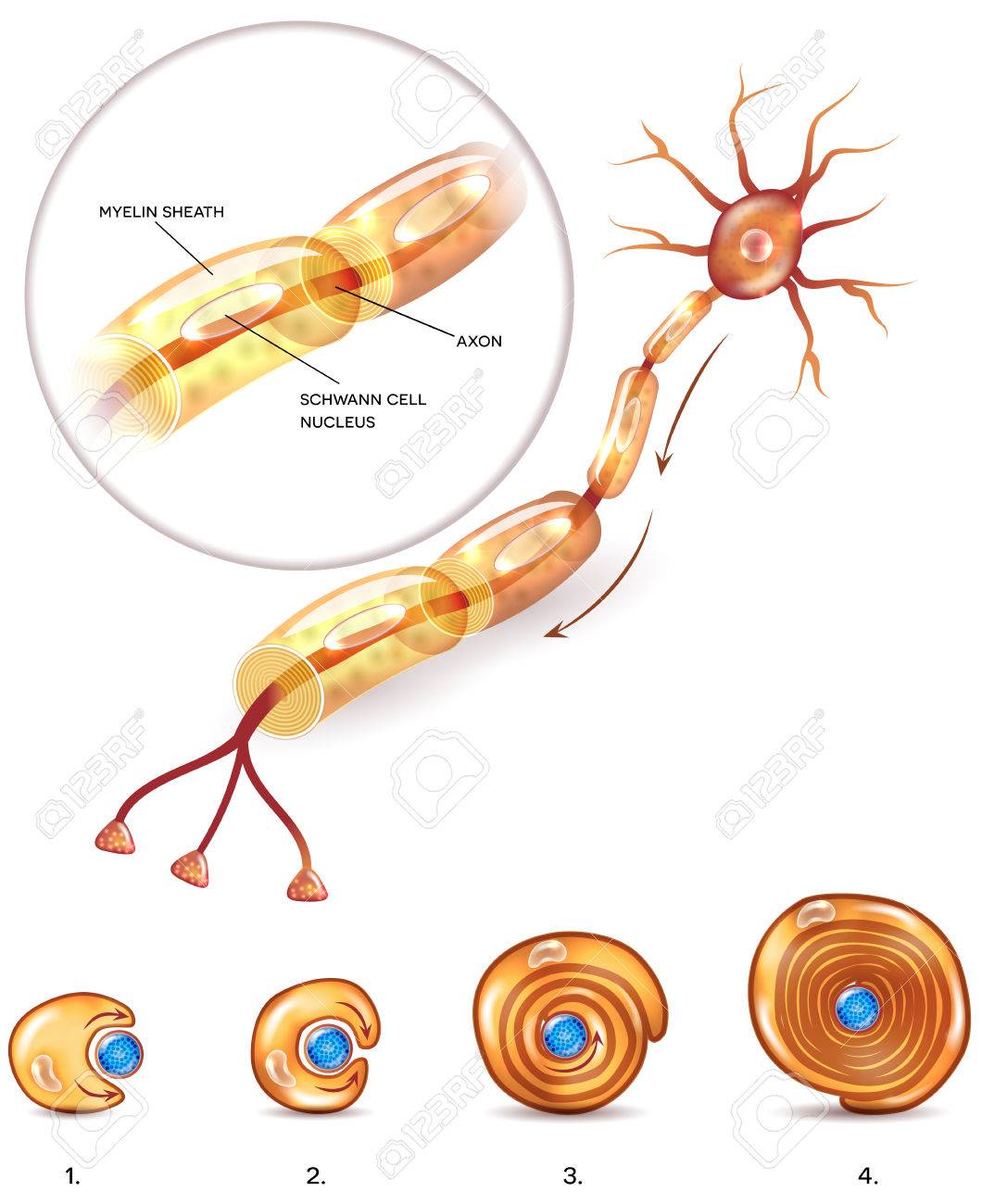 Neuron Anatomy 3d Illustration Close Up And Myelin Sheath Formation
Neuron Anatomy 3d Illustration Close Up And Myelin Sheath Formation
 Neuron Anatomy Activity Worksheet For 7th 12th Grade
Neuron Anatomy Activity Worksheet For 7th 12th Grade
 12 2 Nervous Tissue Anatomy Physiology
12 2 Nervous Tissue Anatomy Physiology
 Anatomy Of The Nervous System Microbiology
Anatomy Of The Nervous System Microbiology

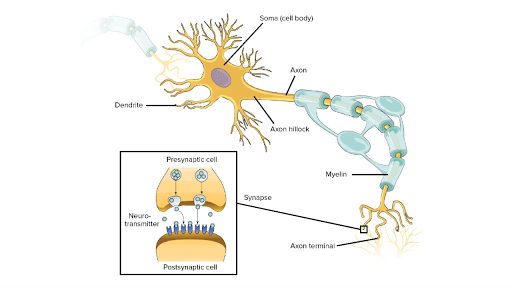
 Cartoon Of Human Neuron Anatomy
Cartoon Of Human Neuron Anatomy
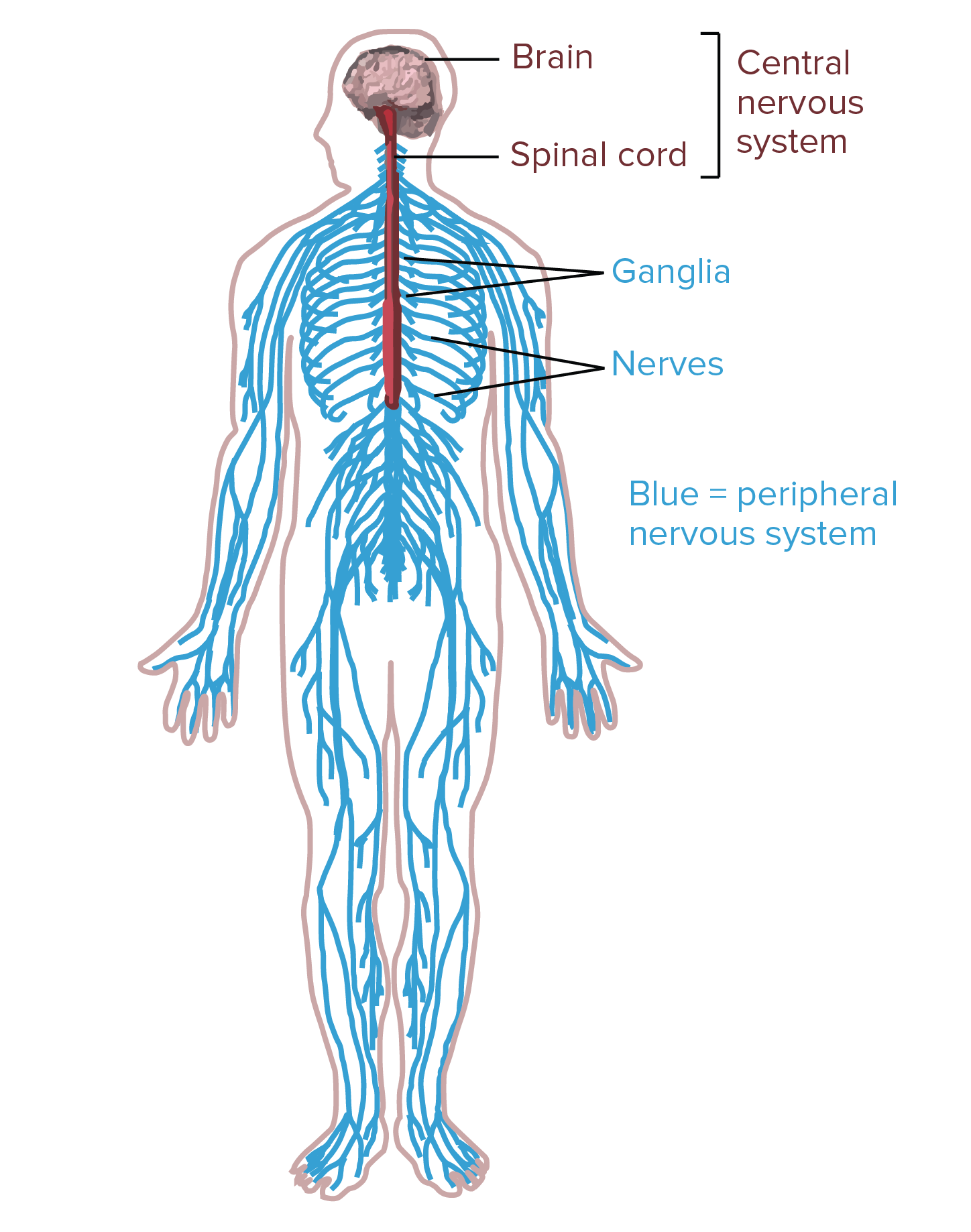 Overview Of Neuron Structure And Function Article Khan
Overview Of Neuron Structure And Function Article Khan
 Neuron Labeling Anatomy And Physiology Diagram Quizlet
Neuron Labeling Anatomy And Physiology Diagram Quizlet
 Week 3 Neuron Anatomy Diagram Quizlet
Week 3 Neuron Anatomy Diagram Quizlet
 Neuron Anatomy Vector Infographic
Neuron Anatomy Vector Infographic
 Neuron Anatomy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Neuron Anatomy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 Nerve Cell Signaling Ppt Download
Nerve Cell Signaling Ppt Download
![]() Neuron Anatomy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Neuron Anatomy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
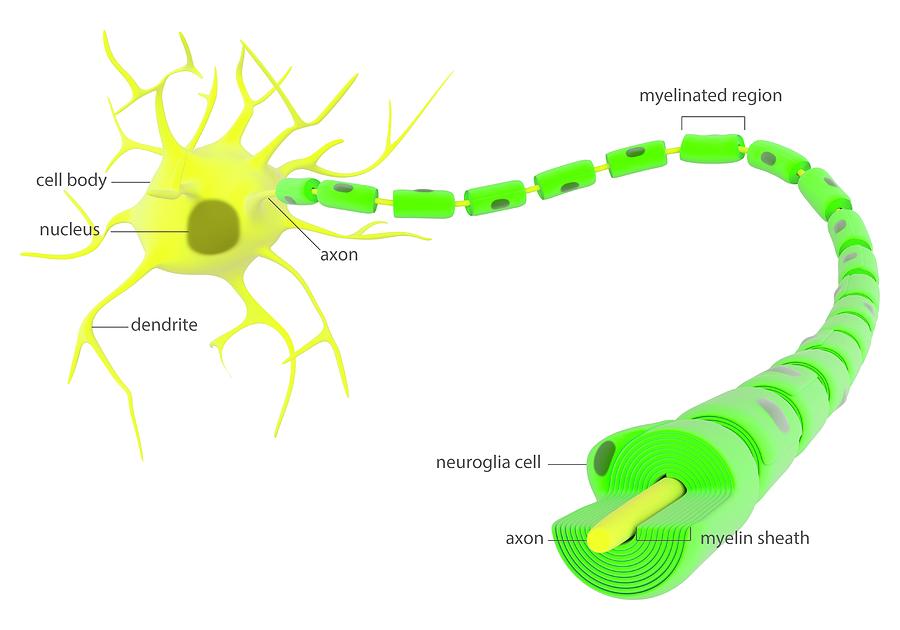


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Neuron Anatomy"
Posting Komentar