Intubation Anatomy
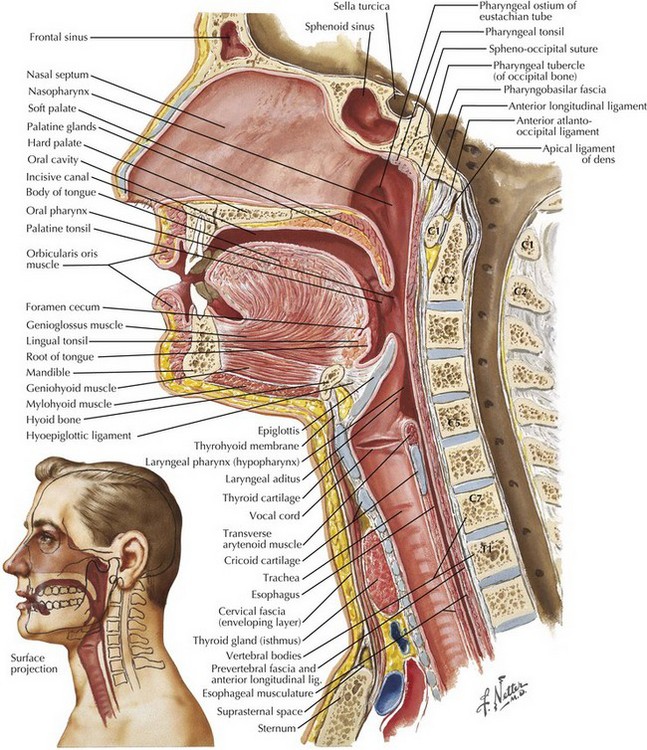
The larynx is a cartilaginous structure slung from the hyoid bone by the hyothyroid membrane. These depressions serve as spit traps.
 Laryngoscopy Intubation Openairway
Laryngoscopy Intubation Openairway
When first learning intubation a beginner often concentrates on memorizing the key laryngeal anatomy.

Intubation anatomy. Navigation best viewed on larger screens. Anaesthesia is then induced using sevoflurane the cuff inflated and if necessary a neuromuscular blocking agent injected. The epiglottic vallecula is a depression vallecula just behind the root of the tongue between the folds in the throat.
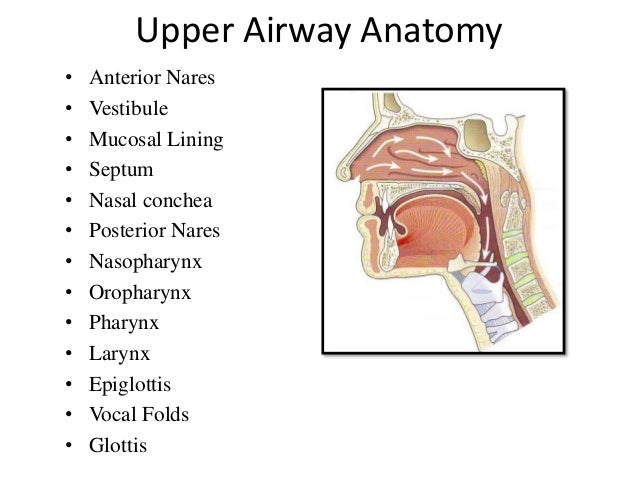
Endotracheal intubation can be performed either orally or nasally although oral intubation is the more commonly used technique5the nasopharynx and oropharynx lead to the laryngopharynx hypopharynx. Tracheal intubation usually simply referred to as intubation is the placement of a flexible plastic tube into the trachea windpipe to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs. Anatomical abnormalities may affect only intubation only airway management or both.
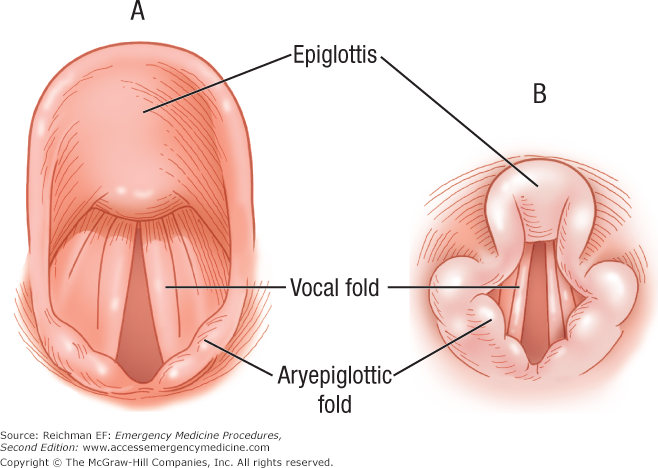
This is important of course. If you cant recognize the vocal cords you will not be able to successfully intubate. The ligaments of the larynx antero lateral view.
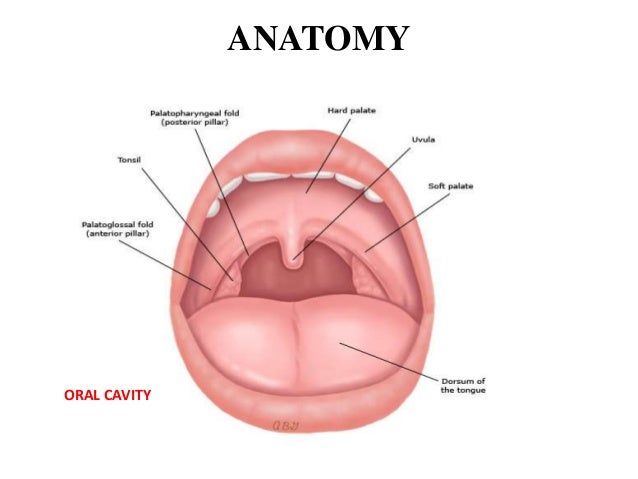
The larynx is the key anatomical structure that needs to be identified when carrying out intubation. It comprises of numerous separate cartilages held together with connective tissue. The nasal fossa is bounded laterally by inferior middle and superior turbinate bones.
Intubation is then performed and tt position is checked by visualization of the carina through the tt and capnography. This section also focuses on the abnormal airways in obesity pregnancy children and neonate and patients with abnormal facial defects. Saliva is temporarily held in the valleculae to prevent initiation of the swallowing reflex.
Nasotracheal intubation is an alternative approach to orotracheal intubation. The two nasal fossae extend from the nostrils to the nasopharynx. The vallecula is an important reference landmark used during intubation of the trachea.
At the base of the tongue the epiglottis separates the larynx from the laryngopharynx. Try using search on phones and tablets. The nasal fossae are divided by the midline cartilaginous septum and medial portions of the lateral cartilages fig.
 Chapter 6 Essential Anatomy Of The Airway Emergency
Chapter 6 Essential Anatomy Of The Airway Emergency
Intubation Causes Symptoms Treatment Intubation
 Airway Intubation Stock Photos Airway Intubation Stock
Airway Intubation Stock Photos Airway Intubation Stock
 Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
 1 Endotracheal Intubation Extubati On 2 Upper Airway
1 Endotracheal Intubation Extubati On 2 Upper Airway
 Chapter 122 Intubation And Airway Support Principles And
Chapter 122 Intubation And Airway Support Principles And
 Classic Intubation And Tracheostomy Procedures Medical
Classic Intubation And Tracheostomy Procedures Medical
 Intubation And Mechanical Ventilation 22 Dr Virbhan Balai
Intubation And Mechanical Ventilation 22 Dr Virbhan Balai
 Tracheal Intubation And Endoscopic Anatomy Basicmedical Key
Tracheal Intubation And Endoscopic Anatomy Basicmedical Key
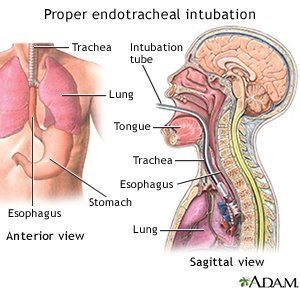
 Endotracheal Intubation Vs Esophageal Intubation Medical
Endotracheal Intubation Vs Esophageal Intubation Medical
 Intubation Preparation And Equipment Paediatric Emergencies
Intubation Preparation And Equipment Paediatric Emergencies
 Insertion Of An Endotracheal Tube What You Need To Know
Insertion Of An Endotracheal Tube What You Need To Know
Throat Anatomy And Endotracheal Intubation
 Sagittal Section Of An Alpaca Head Showing Pertinent Anatomy
Sagittal Section Of An Alpaca Head Showing Pertinent Anatomy
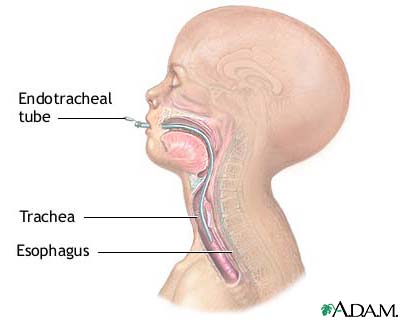 Endotracheal Intubation Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
Endotracheal Intubation Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
 Barbra Villona On Twitter Nice Intubation Anatomy Graphic
Barbra Villona On Twitter Nice Intubation Anatomy Graphic
Essential Procedures For Emergency Urgent And Primary Care
 1 Oral Tracheal Intubation Download Scientific Diagram
1 Oral Tracheal Intubation Download Scientific Diagram
 Airway Procedures Resuscitation Harwood Nuss Clinical
Airway Procedures Resuscitation Harwood Nuss Clinical
 Correct Endotracheal Vs Incorrect Esophageal Intubation
Correct Endotracheal Vs Incorrect Esophageal Intubation
 Intubation Procedure Video Endotracheal
Intubation Procedure Video Endotracheal
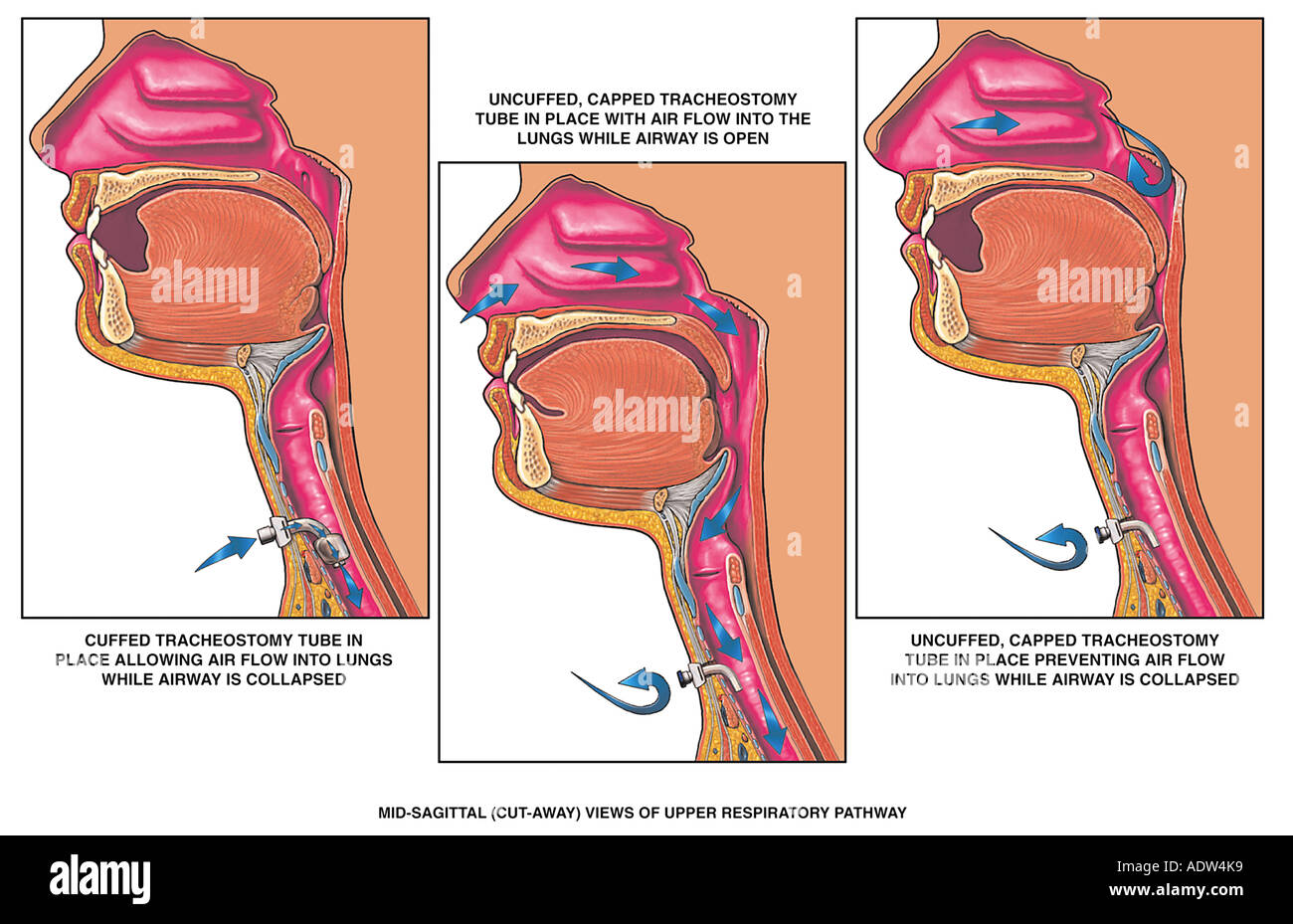
Endotracheal Intubation Anatomy Of Pathway Medical
 Chapter 38 Airway Management Principles And Practice Of
Chapter 38 Airway Management Principles And Practice Of
 Midface Reduction Fixation Special Considerations
Midface Reduction Fixation Special Considerations
 Endotracheal Intubation In Oral Maxillofacial Surgery
Endotracheal Intubation In Oral Maxillofacial Surgery



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Intubation Anatomy"
Posting Komentar