Auricular Anatomy
Aperture is the entrance to the ear canal. Usually this is caused by an infection.
 Ear Anatomy Physiology Wikivet English
Ear Anatomy Physiology Wikivet English
Just pick an audience or yourself and itll end up in their incoming play queue.

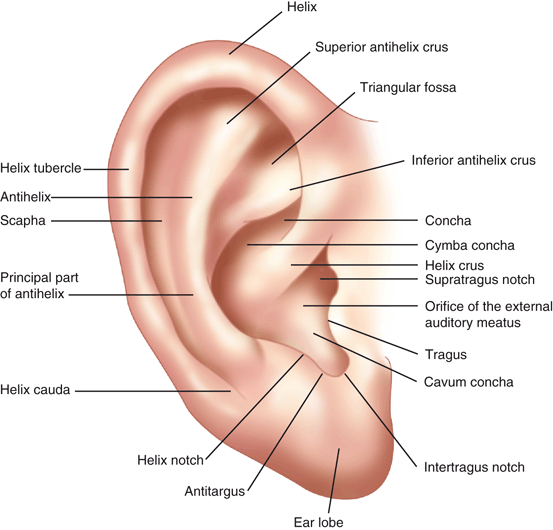
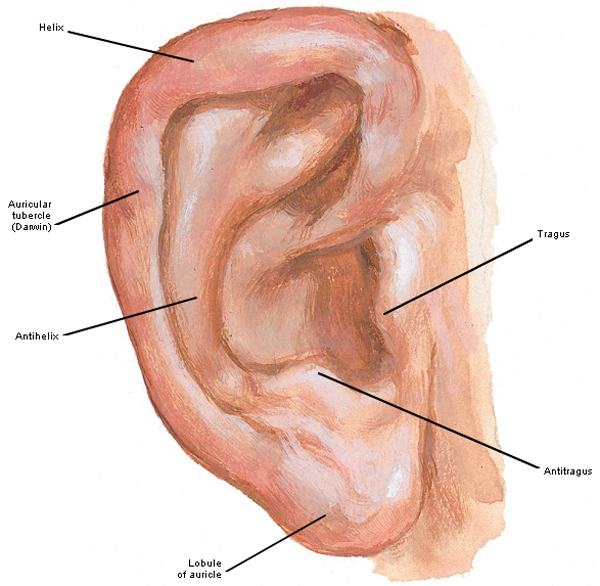
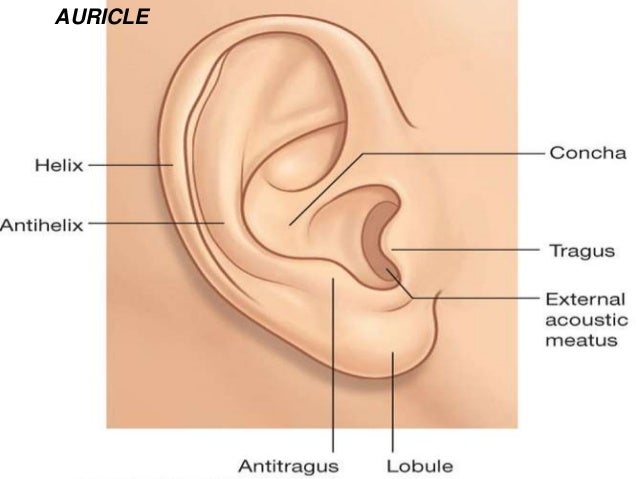
Auricular anatomy. Also called auricle outer ear called the ear the shell shaped part surrounding the auditory canal ceruminous glands outer ear in skin lined walls which secrete a waxy yellow substance earwax or cerumen. The middle ear contains three bones the malleus incus and stapes that amplify the sound. Antihelix forms a y shape where the upper parts are.
Some of these are serious some are not serious. The cochlea is shaped like a snail and is divided into two chambers by a membrane. The chambers are full of fluid which vibrates when sound comes in and causes the small hairs which line the membrane to vibrate and send electrical impulses to the brain.
The diagram shows the shape and location of most of these components. Inflammation or infection of the middle ear behind the eardrum. Greater auricular nerve branch of the cervical plexus innervates the skin of the auricle.
The outer ear includes. Ear anatomy inner ear. Auricle cartilage covered by skin placed on opposite sides of the head.
Inflammation or infection of the outer ear pinna and ear canal. Auricular sulcus is the depression behind the ear next to the head. Otitis media middle ear inflammation.
Acquired entities can further be delineated into intrinsic processes such as cancer and extrinsic processes such as trauma. Congenital abnormalities of the ear are common and largely affect the shape of the auricle. Auditory canal also called the ear canal.
Swimmers ear otitis externa. Lesser occipital nerve branch of the cervical plexus innervates the skin of the auricle. The cochlea which is the hearing portion and the semicircular canals is the balance portion.
Eardrum outer layer also called the tympanic membrane. Auriculotemporal nerve branch. Concha is the hollow.
Antitragus is below the tragus. Pain in the ear can have many causes. The fluid filled inner ear contains the cochleaits job is to translate sound vibrations into electrical signals which are then sent by nerves to the brain.
Variant anatomy of the external ear can be divided into congenital and acquired entities. The sensory innervation to the skin of the auricle comes from numerous nerves. 0 0000 a shoutout is a way of letting people know of a game you want them to play.
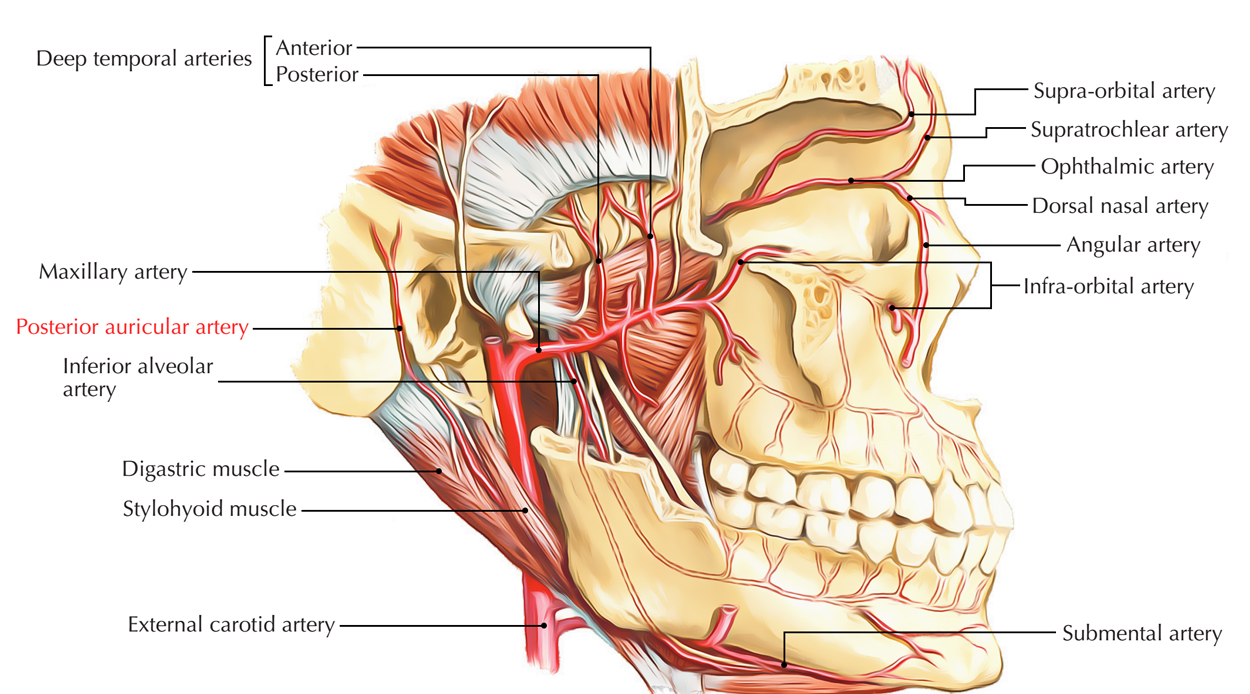 Posterior Auricular Artery Earth S Lab
Posterior Auricular Artery Earth S Lab
 The Posterior Auricular Anatomy Download Scientific Diagram
The Posterior Auricular Anatomy Download Scientific Diagram
 Figure Post Auricular Artery Image Courtesy O Chaigasame
Figure Post Auricular Artery Image Courtesy O Chaigasame
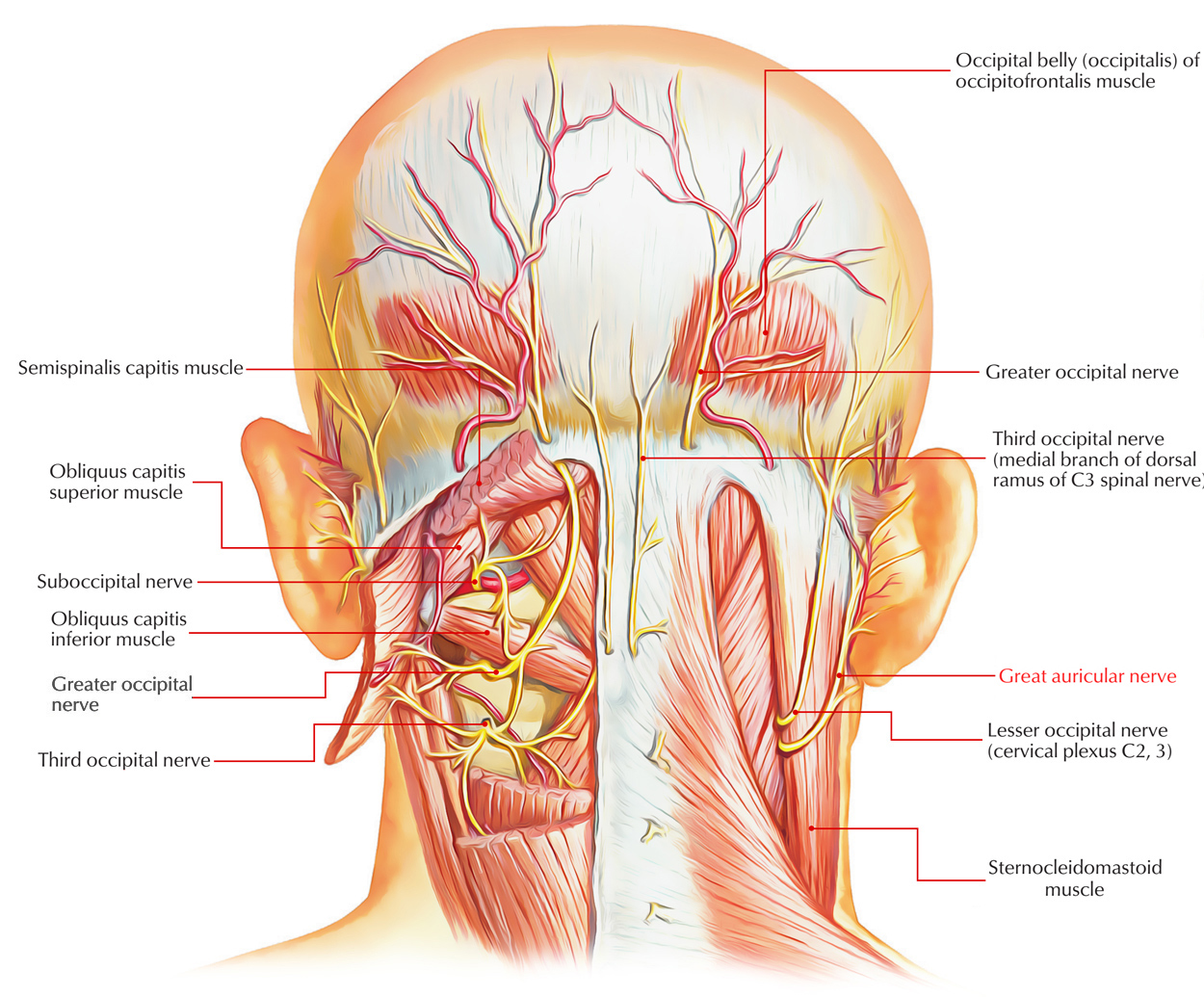 Great Auricular Nerve Earth S Lab
Great Auricular Nerve Earth S Lab
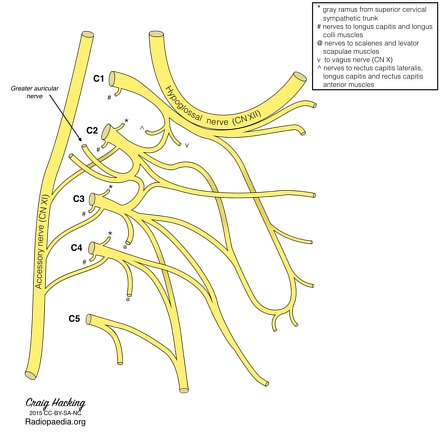 Greater Auricular Nerve Radiology Reference Article
Greater Auricular Nerve Radiology Reference Article
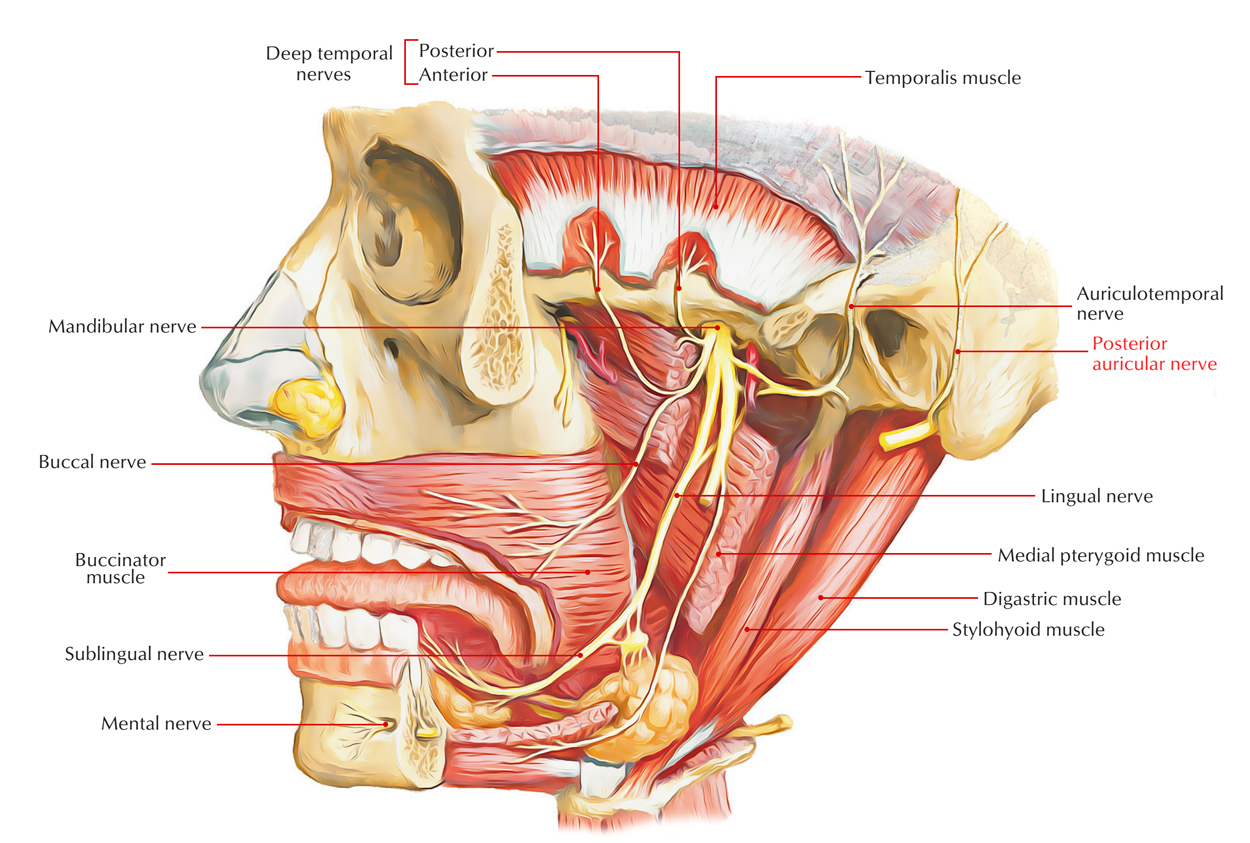 Posterior Auricular Nerve Earth S Lab
Posterior Auricular Nerve Earth S Lab
 Posterior Auricular Nerve Wikipedia
Posterior Auricular Nerve Wikipedia
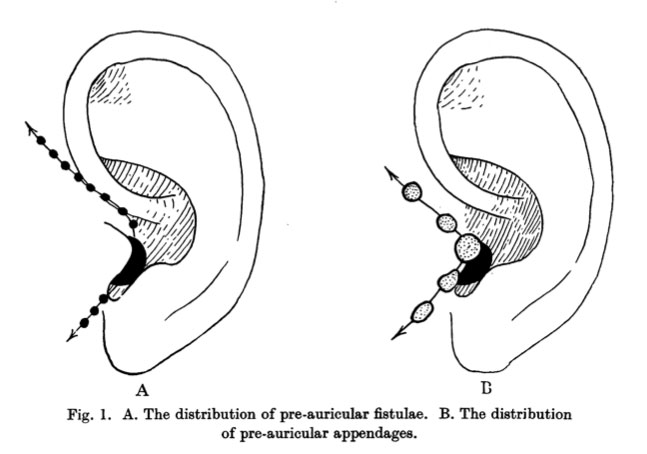 Hearing Outer Ear Development Embryology
Hearing Outer Ear Development Embryology
 Auricle Anatomy Google 검색 External Ear Anatomy Ear
Auricle Anatomy Google 검색 External Ear Anatomy Ear
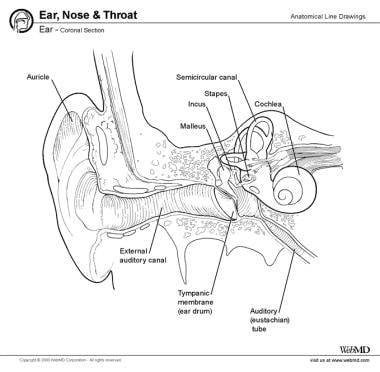 Ear Anatomy Overview Embryology Gross Anatomy
Ear Anatomy Overview Embryology Gross Anatomy
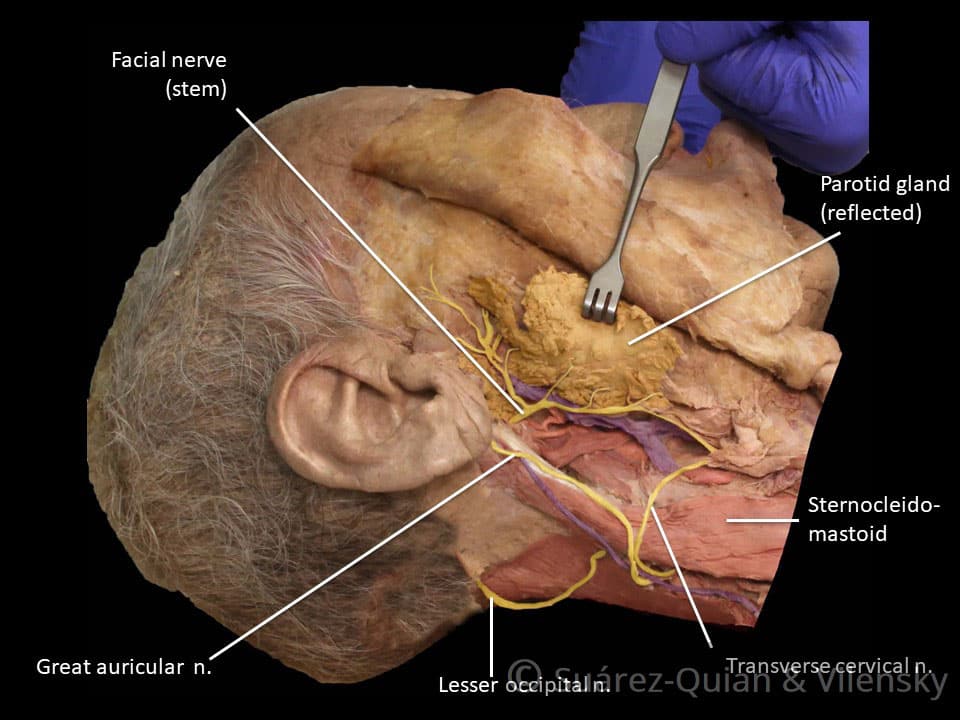 The Facial Nerve Cn Vii Course Functions Teachmeanatomy
The Facial Nerve Cn Vii Course Functions Teachmeanatomy
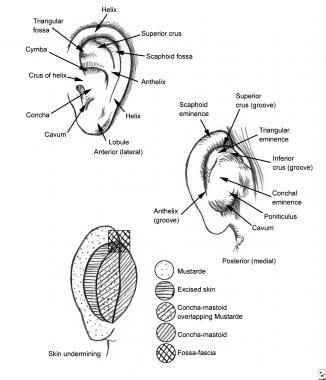 Prominent Ear Background History Of The Procedure Problem
Prominent Ear Background History Of The Procedure Problem
 Auricular Chondritis Definition Symptoms Treatment
Auricular Chondritis Definition Symptoms Treatment
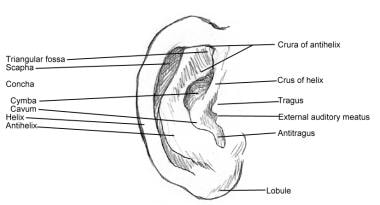 Ear Anatomy Overview Embryology Gross Anatomy
Ear Anatomy Overview Embryology Gross Anatomy
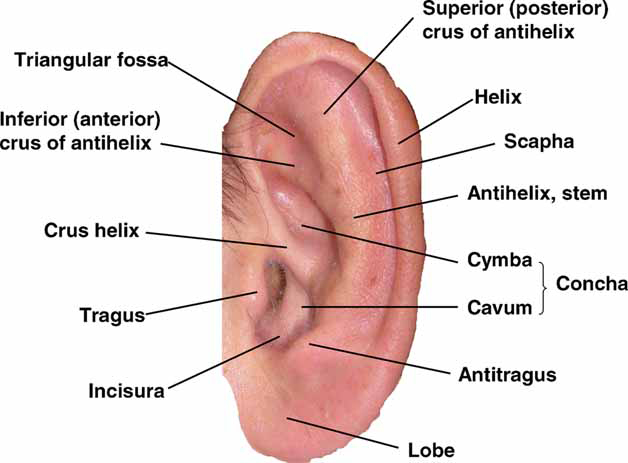 Elements Of Morphology Human Malformation Terminology
Elements Of Morphology Human Malformation Terminology
 Auricular Internal Body Points Chart
Auricular Internal Body Points Chart
 Auricular Acupuncture Chart Chinese Medicine Theory Yin
Auricular Acupuncture Chart Chinese Medicine Theory Yin
 Ear Anatomy And Hearing Loss Beltone Tristate
Ear Anatomy And Hearing Loss Beltone Tristate
 Left Auricle Anatomy Pictures And Information
Left Auricle Anatomy Pictures And Information
 Occipital Artery An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Occipital Artery An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
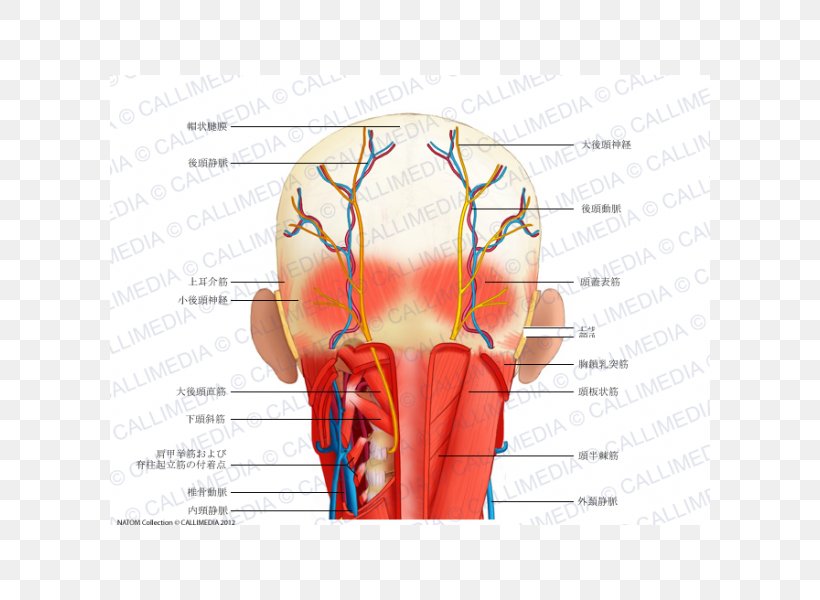 Head And Neck Anatomy Human Head Muscle Png 600x600px
Head And Neck Anatomy Human Head Muscle Png 600x600px
Audiology Specialists Anatomy Of The Ear
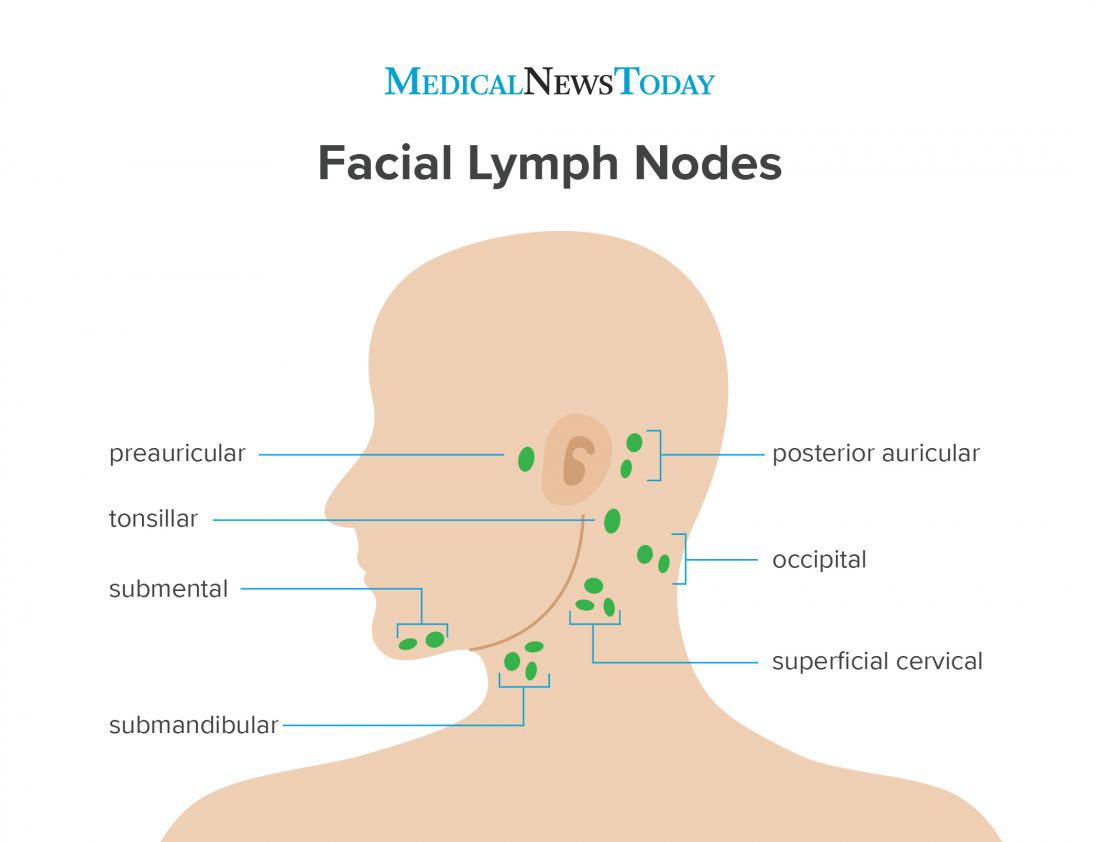 Preauricular Lymph Nodes Causes Of Swelling
Preauricular Lymph Nodes Causes Of Swelling
 Auricular Acupuncture Springerlink
Auricular Acupuncture Springerlink
 Surgery Of The Auricle And Ear Canal Ento Key
Surgery Of The Auricle And Ear Canal Ento Key


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Auricular Anatomy"
Posting Komentar