Anatomy Of Elbow Joint
The ends of the bones are covered with cartilage. In conjunction with the shoulder joint and wrist the elbow gives the arm much of its versatility as well as structure and durability.
The elbow is a hinged joint made up of three bones the humerus ulna and radius.
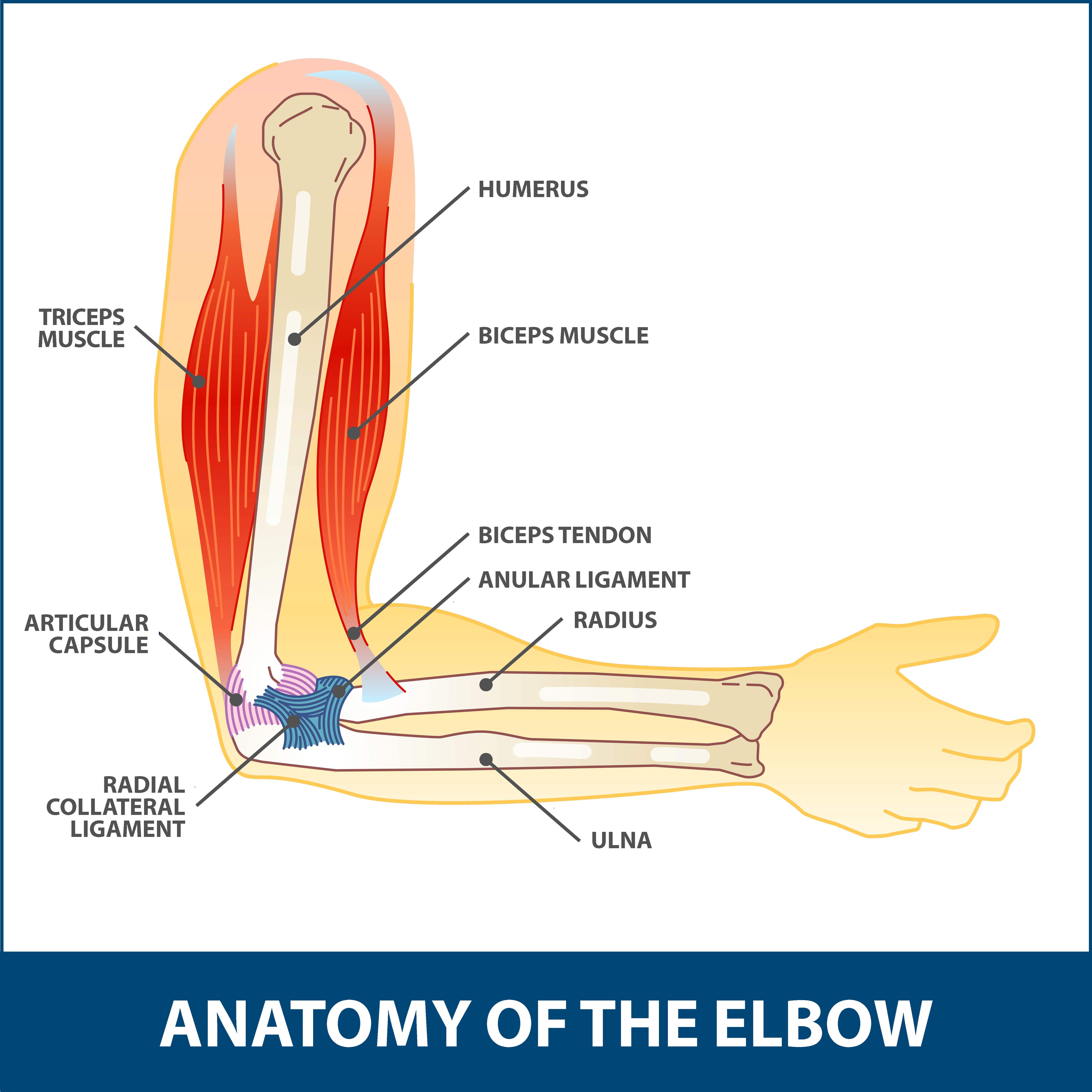
Anatomy of elbow joint. Henry has demonstrated that their relationship and location can be approximated by placing the opposing thumb and the index long. The unique positioning and interaction of the bones in the joint allows for a small amount of rotation as well as hinge action. There are three main flexor muscles at the elbow.
The elbow is one of the largest joints in the body. Brachialis originates from the distal half of the anterior surface of the humerus. The muscles comprising the contour of the medial anterior forearm include the pronator teres flexor carpi radialis palmaris longus and flexor carpi ulnaris.
Brachialis acts exclusively as an elbow flexor and is one of the few muscles in. Anatomy of the elbow the elbow is a hinge joint made up of the humerus ulna and radius. Biceps brachii is the main elbow flexor but as a biarticular.
The anatomy of the elbow. The elbow is where the two bones of the forearm the radius on the thumb side of the arm and the ulna on the pinky finger side meet the bone of the upper arm the humerus. Cartilage has a rubbery consistency that allows the joints to slide easily against one another and absorb shock.
Anatomy of the elbow joint. Movements at a hinge joint biceps brachii originates as two heads. The elbow joint is a complex hinge joint formed between the distal end of the humerus in the upper arm and the proximal ends of the ulna and radius in the forearm.
The elbow allows for the flexion and extension of the forearm relative to the upper arm as well as rotation of the forearm and wrist. Extension triceps brachii and anconeus. Brachioradialis acts essentially as an elbow flexor but also supinates during extreme pronation.
Flexion brachialis biceps brachii brachioradialis. There are two muscles in this compartment that produce flexion at the elbow joint. The synovial lining covers the internal surface of the fibrous joint capsule and the nonarticular surfaces of the joint that are located intracapsularly.
The bones are held together with ligaments that form the joint capsule. The elbow joint has a synovial membranelined joint capsule that is contiguous between the hinge and radioulnar aspects of the joint. The orientation of the bones forming the elbow joint produces a hinge type synovial joint which allows for extension and flexion of the forearm.
An inside look at the structure of the elbow.
 Elbow Forearm Atlas Of Anatomy
Elbow Forearm Atlas Of Anatomy
 Common Elbow Conditions Pro Sports Orthopedics
Common Elbow Conditions Pro Sports Orthopedics
 Anatomy 101 Elbow Tendons The Handcare Blog
Anatomy 101 Elbow Tendons The Handcare Blog
 Elbow Joint Anatomy Bones Synovial Membrane Ligaments
Elbow Joint Anatomy Bones Synovial Membrane Ligaments
 1 Anatomy Of The Elbow Joint Double Conic Frustum
1 Anatomy Of The Elbow Joint Double Conic Frustum
 Elbow Forearm Atlas Of Anatomy
Elbow Forearm Atlas Of Anatomy
 9 6 Anatomy Of Selected Synovial Joints Anatomy And Physiology
9 6 Anatomy Of Selected Synovial Joints Anatomy And Physiology
 Elbow Joint Cross Section Anatomy Diagram Clip Art
Elbow Joint Cross Section Anatomy Diagram Clip Art
 Total Elbow Joint Replacement Direct Orthopedic Care
Total Elbow Joint Replacement Direct Orthopedic Care
 The Elbow Joint Mobility Health
The Elbow Joint Mobility Health
 Elbow Anatomy Animated Tutorial
Elbow Anatomy Animated Tutorial
 Ppt Elbow Joint Powerpoint Presentation Free Download
Ppt Elbow Joint Powerpoint Presentation Free Download
 Anatomy Musculoskeletal Ultrasonography
Anatomy Musculoskeletal Ultrasonography
 Anatomy Of The Elbow Elbow Anatomy
Anatomy Of The Elbow Elbow Anatomy
 Ligaments Of Elbow Ligaments Of The Right Elbow Joint
Ligaments Of Elbow Ligaments Of The Right Elbow Joint
 Total Elbow Replacement Orthoinfo Aaos
Total Elbow Replacement Orthoinfo Aaos
 Elbow Joint Anatomy Movement Muscle Involvement Elbow
Elbow Joint Anatomy Movement Muscle Involvement Elbow
 Arthroscopic Debridement Elbow Florida Orthopaedic Institute
Arthroscopic Debridement Elbow Florida Orthopaedic Institute
 Elbow Muscular Anatomy Musculoskeletal Learning Portfolio
Elbow Muscular Anatomy Musculoskeletal Learning Portfolio

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Elbow Joint"
Posting Komentar