Orbital Anatomy
From the medial orbital rim to apex the orbit measures approximately 45 mm in length whereas from the lateral orbital rim to the apex the measurement is approximately 1 cm shorter. The orbital floor is the most frequently fractured wall in trauma where an object larger than the orbit such as a ball or fist impacts the entire orbit.
 Orbital Tumors Weill Cornell Brain And Spine Center
Orbital Tumors Weill Cornell Brain And Spine Center
The orbital floor is the only wall of the orbit that does not contain part of the sphenoid bone.
Orbital anatomy. The lacrimal system produces distributes and drains tears. The orbit which protects supports and maximizes the function of the eye. Orbital process of the frontal bone orbital process of the zygomatic bone.
The childs orbit is rounder but with age the width increases. The orbit can be thought of as a pyramidal structure. Orbit anatomy in anatomy the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated.
Use the mouse scroll wheel to move the images up and down alternatively use the tiny arrows on both side of the image to move the images. The contents of the orbit are separated and supported by multiple. The bony orbit borders and anatomical relations.
Inferior orbital fissure lies between. This fissure allows the passage to the nerves iii iv vi branches of the v1 and ophthalmic veins. Orbital anatomy the orbital cavities are large bony sockets that house the eyeballs with associated muscles nerves blood vessels and fat.
In the adult human the volume of the orbit is 30 millilitres 106 imp fl oz. 101 us fl oz. Orbit can refer to the bony socket or it can also be used to imply the contents.
Orbit and attitude tracking. Fig 11 diagram of the arterial supply to the eye. Orbit anatomy orbit celestial mechanics orbit celestial mechanics orbit celestial mechanics orbit disambiguation orbit disambiguation orbit group theory orbit physics orbit physics orbit physics orbit adjust propulsion system.
Pathways into the orbit. Each orbit is pear shaped with the optic nerve representing the stem. This mri orbits and paranasal sinuses cross sectional anatomy tool is absolutely free to use.
The widest circumference of the orbit is inside the orbital rim at the lacrimal recess. Superior orbital fissure lies between the lesser and the greater wing of sphenoid. Fig 12 the major openings into the orbit.
Orbital Anatomy Ophthalmology Review
 Figure 1 From Surgical Orbital Anatomy Semantic Scholar
Figure 1 From Surgical Orbital Anatomy Semantic Scholar
 Schematic Anatomy Of The Human Orbit In Transverse Cross
Schematic Anatomy Of The Human Orbit In Transverse Cross
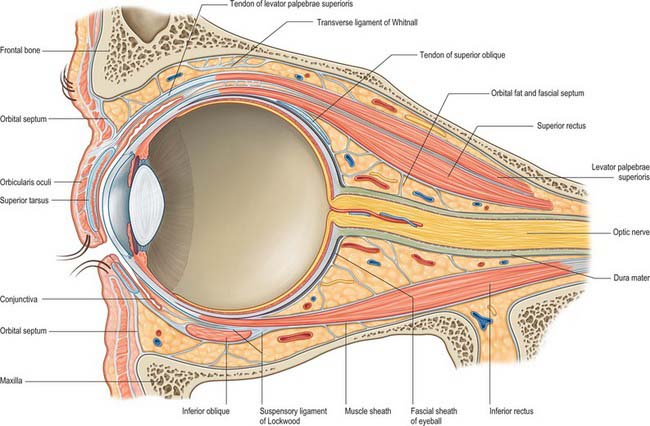 The Orbit And Accessory Visual Apparatus Basicmedical Key
The Orbit And Accessory Visual Apparatus Basicmedical Key
 Orbital Anatomy Plastic Surgery Key
Orbital Anatomy Plastic Surgery Key
 Use Of High Resolution Microscopy Coil Mri For Depicting
Use Of High Resolution Microscopy Coil Mri For Depicting
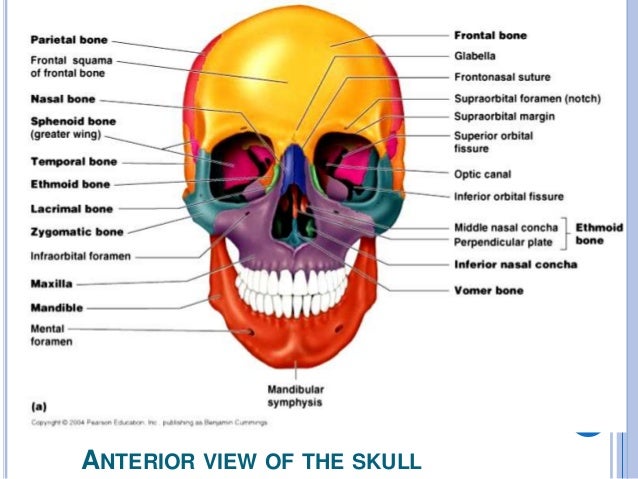
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/777/IOA26SbYNKr5nhVqAvklQ_bones-of-the-orbit_english.jpg) Bones Of The Orbit Anatomy Foramina Walls And Diagram
Bones Of The Orbit Anatomy Foramina Walls And Diagram
 Anatomy Of The Eye And Orbit The Clinical Essentials
Anatomy Of The Eye And Orbit The Clinical Essentials
 Upper Eyelid Anatomy 2019 Update
Upper Eyelid Anatomy 2019 Update
 The Accessory Organs Of The Eye Human Anatomy
The Accessory Organs Of The Eye Human Anatomy
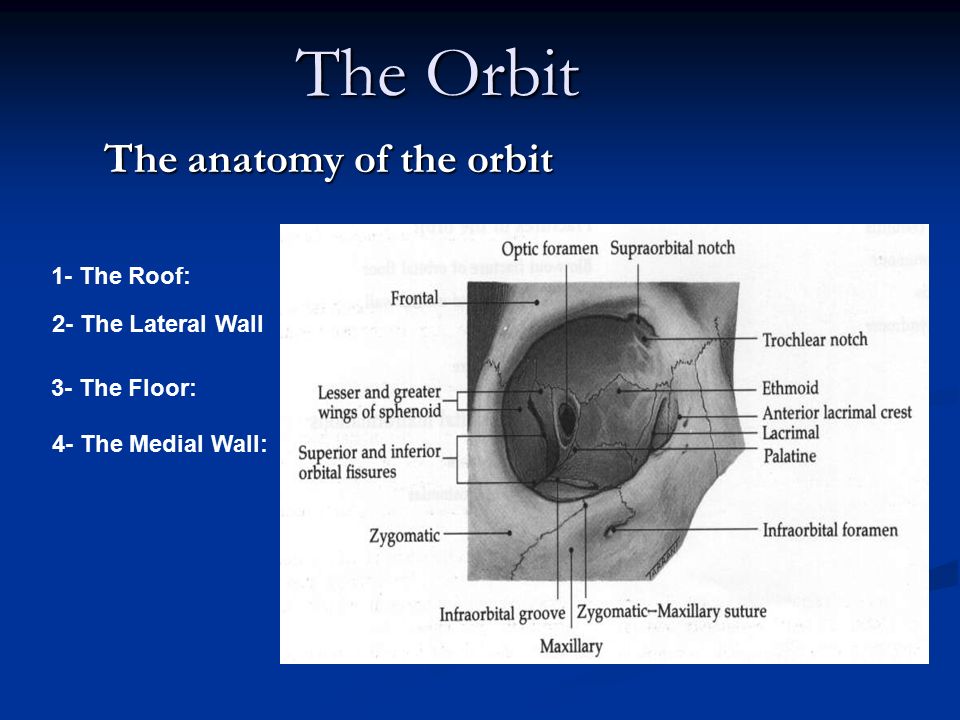 The Anatomy Of The Orbit Ppt Download
The Anatomy Of The Orbit Ppt Download

 Ecr 2013 C 2011 Pictorial Review Of Extraconal And
Ecr 2013 C 2011 Pictorial Review Of Extraconal And
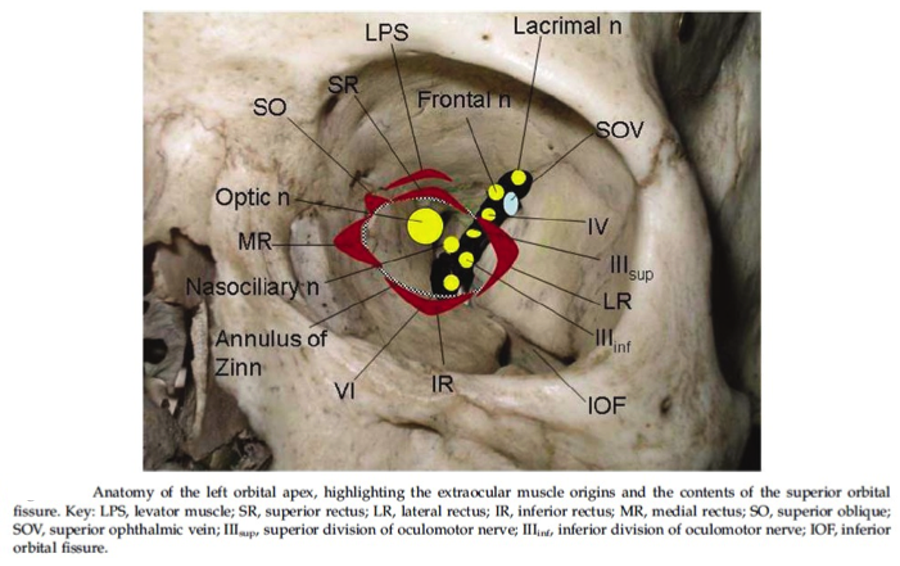 Cureus A Clinical Review Of Orbital Anatomy And Its
Cureus A Clinical Review Of Orbital Anatomy And Its
 Orbits And Eyes Anatomical Illustrations
Orbits And Eyes Anatomical Illustrations
 Orbital Bone Bones Muscles Joints Medical Anatomy
Orbital Bone Bones Muscles Joints Medical Anatomy
 Us 46 6 Eye With Orbit Eye And Orbital Anatomy Model Eye Model In Medical Science From Office School Supplies On Aliexpress
Us 46 6 Eye With Orbit Eye And Orbital Anatomy Model Eye Model In Medical Science From Office School Supplies On Aliexpress
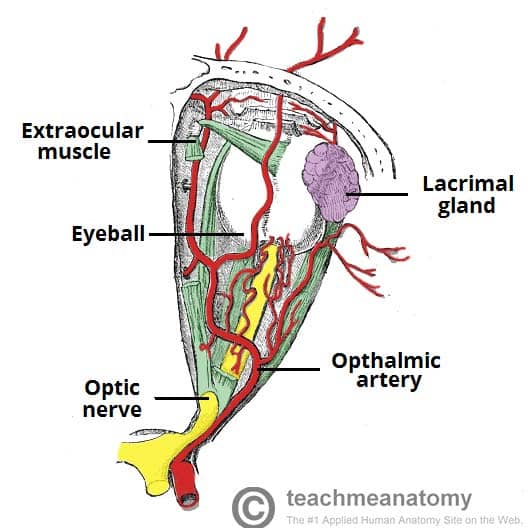 The Bony Orbit Borders Contents Fractures Teachmeanatomy
The Bony Orbit Borders Contents Fractures Teachmeanatomy
 Anatomy The Orbit Flashcards Quizlet
Anatomy The Orbit Flashcards Quizlet
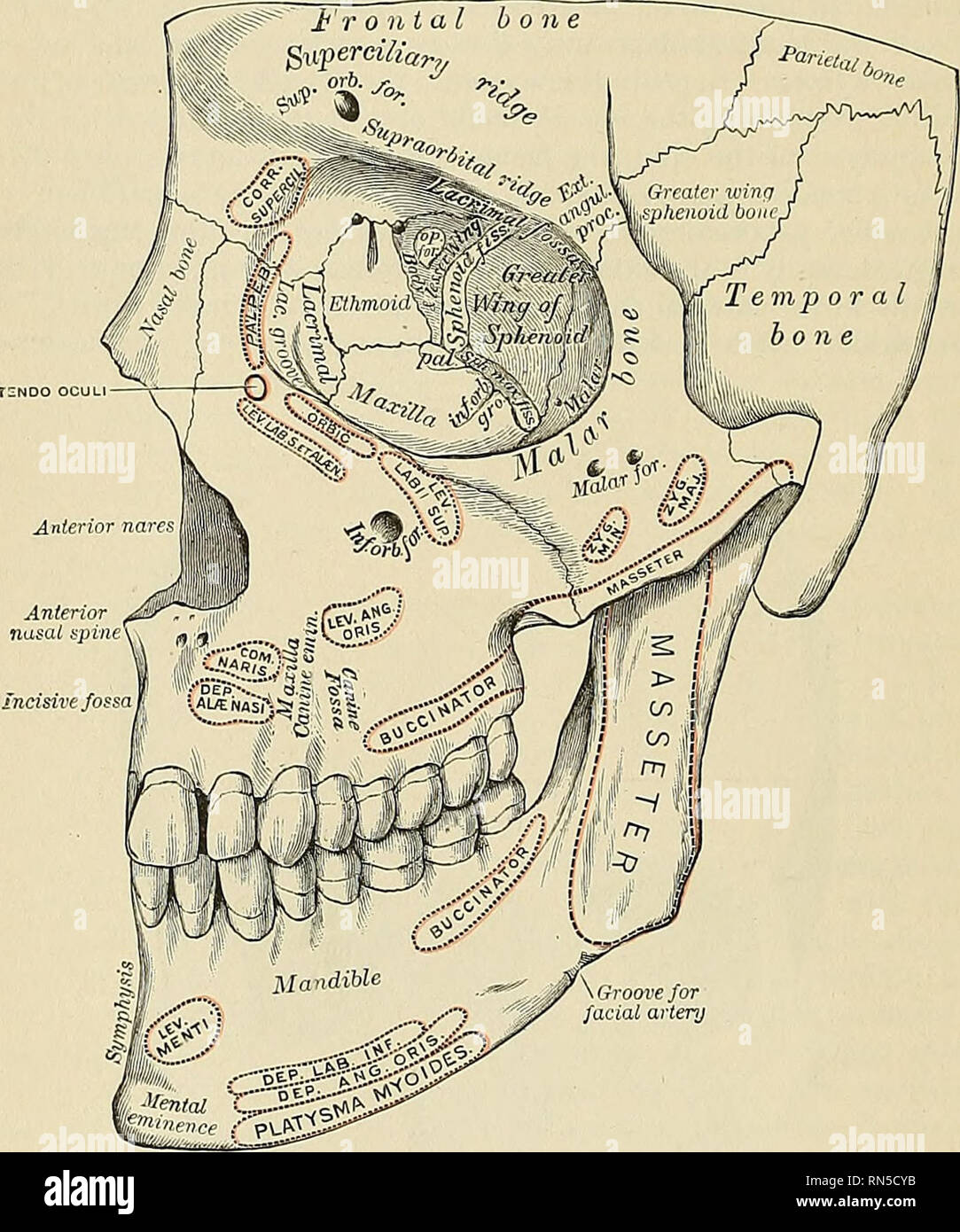
 Anatomy Descriptive And Applied Anatomy 136 Special
Anatomy Descriptive And Applied Anatomy 136 Special
 Skull Bones Of The Orbit Human Anatomy Kenhub
Skull Bones Of The Orbit Human Anatomy Kenhub
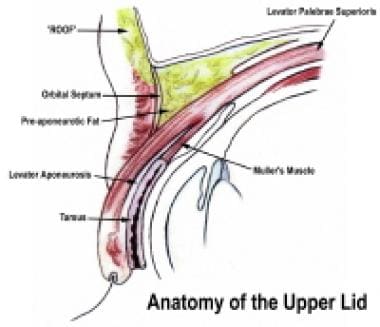 What Is The Anatomy Of Orbital Septum Relevant To
What Is The Anatomy Of Orbital Septum Relevant To
 Periorbital And Orbital Cellulitis Pediatrics Clerkship
Periorbital And Orbital Cellulitis Pediatrics Clerkship
 Orbits And Eyes Anatomical Illustrations
Orbits And Eyes Anatomical Illustrations
 Anatomy Of The Eye Orbit Alila Medical Images
Anatomy Of The Eye Orbit Alila Medical Images
Orbit In Cross Section Anatomy The Eyes Have It

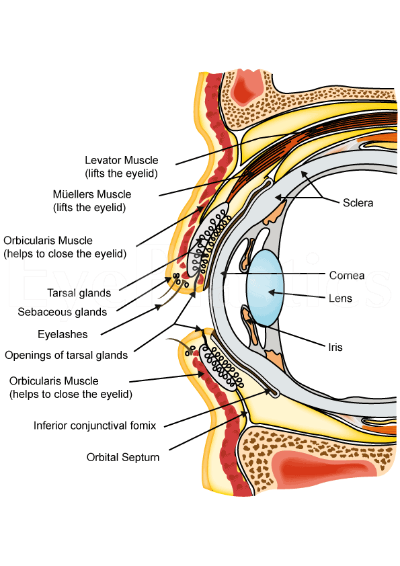


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Orbital Anatomy"
Posting Komentar