Jellyfish Anatomy
The body of an adult jellyfish consists of a bell shaped hood enclosing its internal structure and from which tentacles are suspended. Each tentacle is covered with cells called cnidocytes a type of venomous cell unique to the phylum cnidaria that can sting or kill other animals.
 Anatomy Of A Jellyfish Similar But Different In The Animal
Anatomy Of A Jellyfish Similar But Different In The Animal
Among their many tentacles some jellyfish have parts known as oral arms.

Jellyfish anatomy. Jellyfish are found all over the world from surface waters to the deep sea. The body of a jellyfish features a central axis point. These long appendages move captured prey to the animals mouth which is usually found on the underside of the bell.
They are composed of about 95 percent water. Jellyfish have a complex life cycle. In jellyfish the transparent mesoglea layer is quite thick.
Jellyfish are the simplest swimming animals on earth. Some species have even ditched a mouth entirely. The life cycle of free swimming scyphozoan jellyfish typically consists of three stages.
The medusa is normally the sexual phase the planula larva can disperse widely and is followed by a sedentary polyp phase. The anatomy of a jellyfish is like no other free swimming marine animal. The jellyfish is a simple invertebrate but they are able to move better than others that fall into that same classification.
By contrast humans are about 65 percent water the high water content of jellyfish explains why they immediately collapse into defeated deflated blobs when removed from water. They are well known for their swift and graceful movements through the ocean waters. Jellyfish often called jellies sometimes called jelly fish wrongly because of their soft gelatinous bodies and trailing tentacles are free swimming umbrella shaped marine animals which belong to the phylum cnidaria.
Illustration showing the anatomy of true jellyfish class scyphozoa. The adults are either male or female but in some species they change their sex as they age. A sessile polyp scyphistoma stage asexually buds off young medusae from its upper end with each such ephyra growing into an adult.
These jellies ingest food directly through openings in their oral arms. The anatomy of a jellyfish is very interesting to examine in depth.
 Jellyfish Anatomy Animal Facts And Information
Jellyfish Anatomy Animal Facts And Information
Moon Jellyfish Creationwiki The Encyclopedia Of Creation
 Multimedia Gallery Jellyfish Anatomy Nsf National
Multimedia Gallery Jellyfish Anatomy Nsf National
 Jelly Guide Teal Talk It S About To Get Real
Jelly Guide Teal Talk It S About To Get Real
 Sabah Oceanist The Box Jellyfish Of Sabah Malaysia
Sabah Oceanist The Box Jellyfish Of Sabah Malaysia
 Jellyfishes Marine Biology New Jersey Scuba Diving
Jellyfishes Marine Biology New Jersey Scuba Diving

15 Remarkable Facts About Jellyfish
 Ernst Haeckel Biology Jellyfish Print Scientific Anatomy Illustration Organic Nautical Art Biological Decor Vintage Style Artwork Nh17
Ernst Haeckel Biology Jellyfish Print Scientific Anatomy Illustration Organic Nautical Art Biological Decor Vintage Style Artwork Nh17
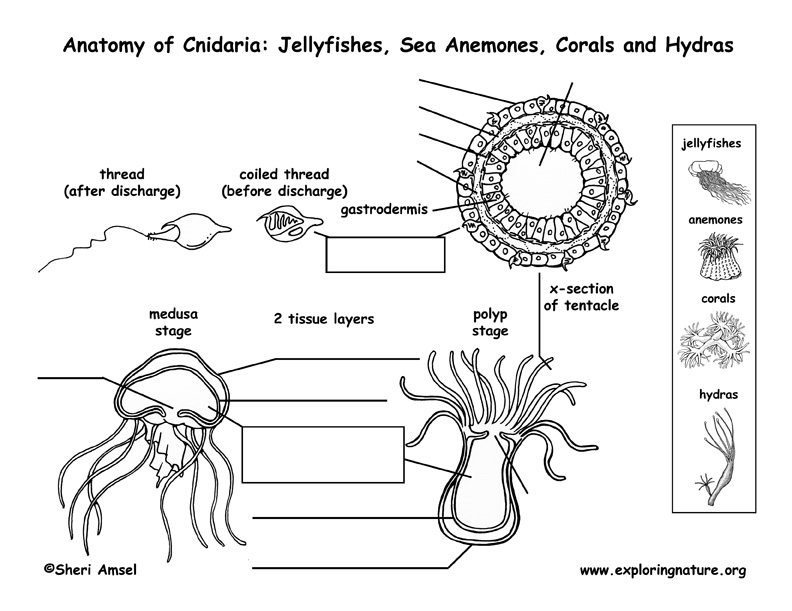 Cnidaria Jellyfish Anemones Corals And Hydras Anatomy
Cnidaria Jellyfish Anemones Corals And Hydras Anatomy
 How Jellyfish Work Howstuffworks
How Jellyfish Work Howstuffworks
 Jellyfish Anatomy 2 These Are From Ocean Park In Hong Kong
Jellyfish Anatomy 2 These Are From Ocean Park In Hong Kong
 Jellyfish Anatomy Google Search Jellyfish Ocean
Jellyfish Anatomy Google Search Jellyfish Ocean
 Cnidarian Structure And Function Advanced Ck 12 Foundation
Cnidarian Structure And Function Advanced Ck 12 Foundation
 Jellyfish External Anatomical Structure
Jellyfish External Anatomical Structure
 Jellyfish Euclid Public Library
Jellyfish Euclid Public Library
 Jellyfish Key Facts Information Pictures
Jellyfish Key Facts Information Pictures
 3 Schematic Of The Internal Anatomy Of The Box Jellyfish
3 Schematic Of The Internal Anatomy Of The Box Jellyfish
Did You Know Jellyfish Are Secretly Planning To Take Over
 3 Jellyfish Body Anatomy Biohold
3 Jellyfish Body Anatomy Biohold
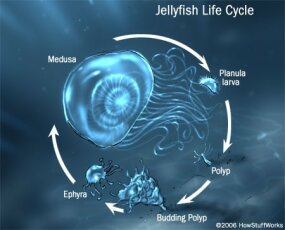 How Jellyfish Work Howstuffworks
How Jellyfish Work Howstuffworks
 Blue Bottle Jellyfish Adaptations Facts Habitat Study Com
Blue Bottle Jellyfish Adaptations Facts Habitat Study Com
 Moon Jellyfish Facts All Five Oceans
Moon Jellyfish Facts All Five Oceans
 In Them We See Our Heart Beat Jellyfish Anatomy A Primer
In Them We See Our Heart Beat Jellyfish Anatomy A Primer
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Jellyfish Anatomy"
Posting Komentar