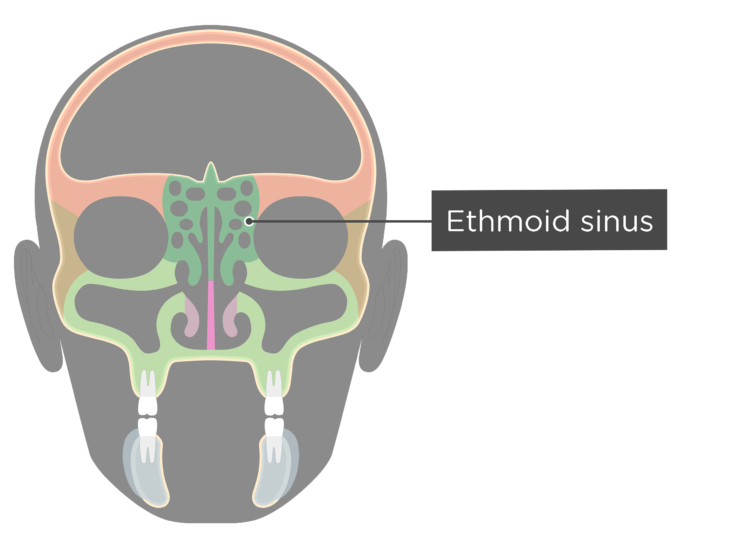
Ethmoid Sinus Anatomy
Your cheekbones hold your maxillary sinuses the largest. The largest sinus cavities are about an inch across.
 Normal Anatomy Ethmoid Sinuses Medical Exhibit
Normal Anatomy Ethmoid Sinuses Medical Exhibit
This article informs about its anatomy and disease conditions.

Ethmoid sinus anatomy. Ninja nerds join us in this video where we show the anatomy of the ethmoid bone through the use of a model. Additionally the ethmoid sinuses are divided into groups of cells by bony basal lamellae. They lie between the upper parts of the nasal cavities and the orbits and are separated from these cavities by thin bony laminae.
The most imporant one is the basal lamellae of the middle turbinate which separates the ethmoid into anterior and posterior groups with different drainage patterns. The ethmoid sinuses are unique because they are the only paranasal sinuses that are more complex than just a single cavity. Between the orbit and the nasal cavity within the ethmoid labyrinth of the ethmoid bone.
Anterior and posterior ethmoidal and supraorbital nerves. Infection of these air cells by bacteria or virus is referred to as ethmoidal sinusitis. Normal anatomy variants.
In addition to creating mucus the sinuses including the ethmoid sinus reduce the skulls overall weight and make ones voice more resonant as they grow in size during puberty. Superior to the ethmoidal sinus is the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal bone laterally the orbit can be found while the nasal cavity is situated medially. The ethmoid bone can be fractured in cases of facial trauma most commonly hitting the dashboard in a collision or a fall from height.
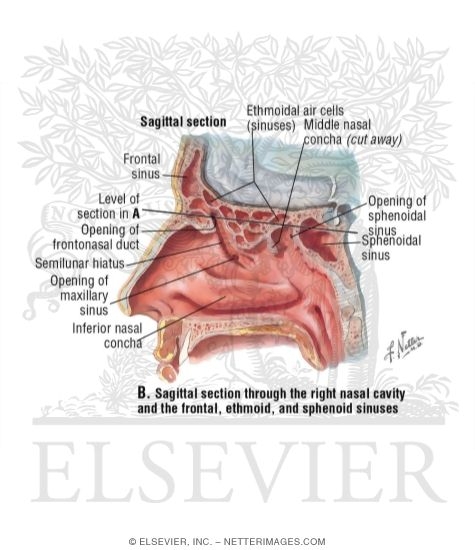
In bones behind your nose are your sphenoid sinuses. The ethmoidal air cells consist of numerous thin walled cavities situated in the ethmoidal labyrinth and completed by the frontal maxilla lacrimal sphenoidal and palatine bones. Please support us go fund me httpswww.
Between your eyes are your ethmoid sinuses. Some signs and symptoms of fracture are related to the anatomy of the ethmoid bone. The ethmoidal sinuses from 3 to 18 thin walled cavities between the nasal cavities and the eye sockets make up the ethmoidal labyrinths.
The low center of your forehead is where your frontal sinuses are located. On each side of the midline. The primary function of the ethmoid sinus like all the sinus cavities in the skull is to provide lubrication mucus to the inner nose.
Others are much smaller. Supraorbital anterior and posterior ethmoidal and sphenopalatine arteries. The ethmoid sinus can have a variable number of air cells.
Ethmoid sinus comprises a group of ethmoidal air cells in the ethmoid bone present between the nose and the eye sockets. Their walls form most of the inner walls of the eye sockets and are joined together by a thin perforated plate of bone at.
 Definition Of Ethmoid Sinus Nci Dictionary Of Cancer Terms
Definition Of Ethmoid Sinus Nci Dictionary Of Cancer Terms
 Sinus Infection Sinusitis Symptoms Signs Treatment
Sinus Infection Sinusitis Symptoms Signs Treatment
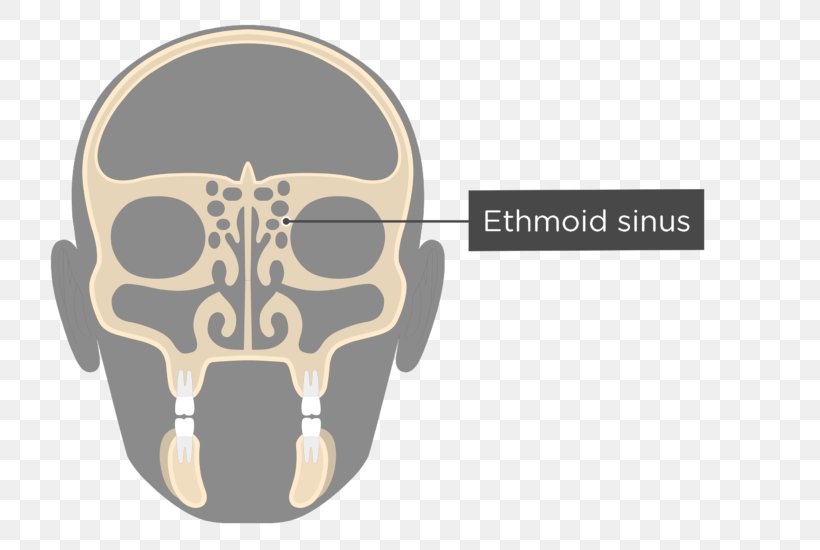 Perpendicular Plate Of Ethmoid Bone Ethmoid Sinus Anatomy
Perpendicular Plate Of Ethmoid Bone Ethmoid Sinus Anatomy
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/cellulae-ethmoidales/DRYEj6XqrVOS97H9fcFOaA_Cellulae_ethmoidales_1.png) Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
 Sinus Cutaway Anatomical Model Lfa 2850
Sinus Cutaway Anatomical Model Lfa 2850
 Ecr 2017 C 2117 Ct Anatomy Of Paranasal Sinuses Epos
Ecr 2017 C 2117 Ct Anatomy Of Paranasal Sinuses Epos
 Patient Resource Publishing Head And Neck Sinus Nasal
Patient Resource Publishing Head And Neck Sinus Nasal
Sinus Ct Scan Sinusitis W S Tichenor M D
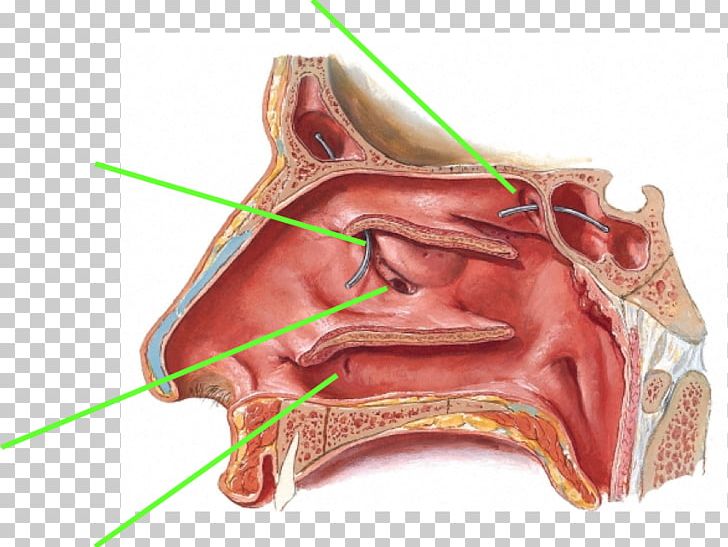 Ethmoid Sinus Ethmoid Bulla Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy Png
Ethmoid Sinus Ethmoid Bulla Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy Png
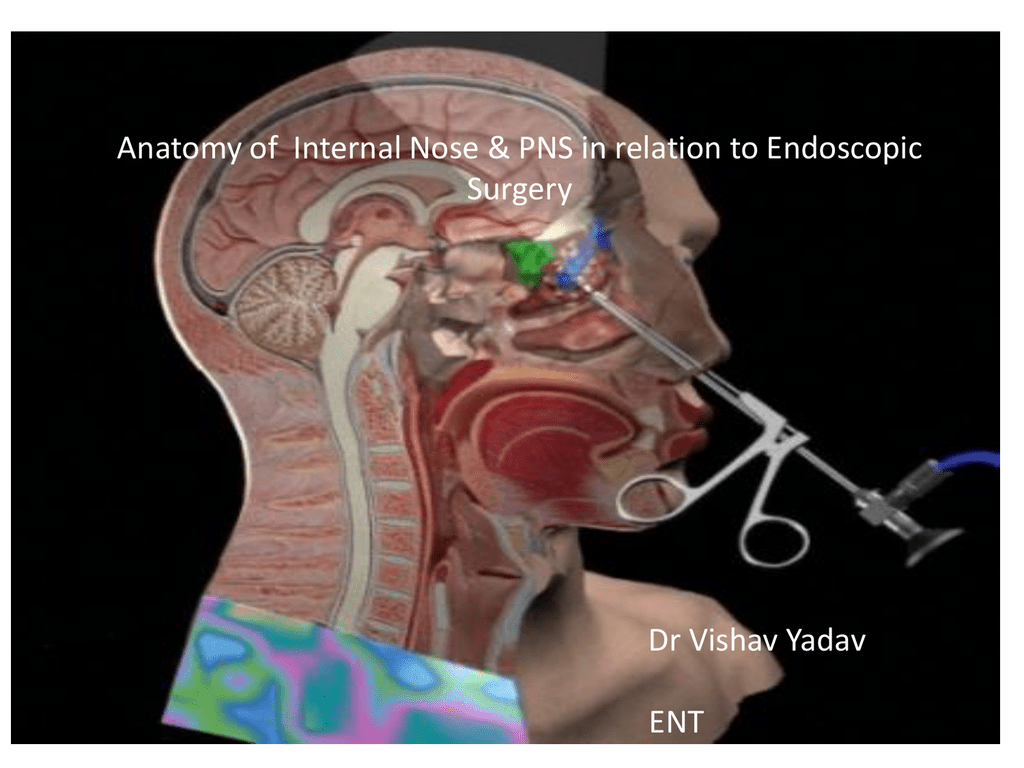
 Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Articles Mount Nittany Health
Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Articles Mount Nittany Health
 Sphenoidal Sinus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Sphenoidal Sinus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Anatomy Paranasal Sinuses Side Views Frontal Stock Vector
Anatomy Paranasal Sinuses Side Views Frontal Stock Vector
Ethmoid Sinus Normal Anatomy Variants
 Staging Of Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinus Cancer
Staging Of Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinus Cancer
 Ethmoid Sinus Iphone Cases Fine Art America
Ethmoid Sinus Iphone Cases Fine Art America
 Ethmoid Sinus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Ethmoid Sinus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Paranasal Sinus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Paranasal Sinus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
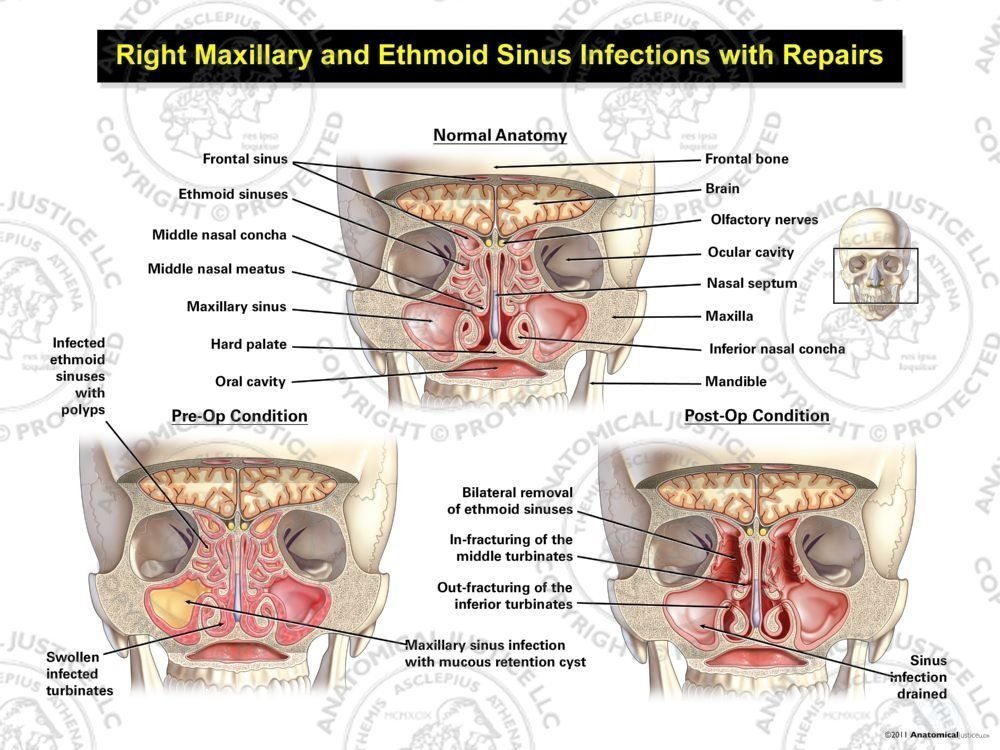 Right Maxillary And Ethmoid Sinus Infections With Repairs
Right Maxillary And Ethmoid Sinus Infections With Repairs

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Ethmoid Sinus Anatomy"
Posting Komentar