Elbow Joint Anatomy
This rotation is easily noticed during activities such as hand to mouth eating motions. The elbow allows for the flexion and extension of the forearm relative to the upper arm as well as rotation of the forearm and wrist.
Anatomical Study On The Innervation Of The Elbow Capsule
The orientation of the bones forming the elbow joint produces a hinge type synovial joint which allows for extension and flexion of the forearm.
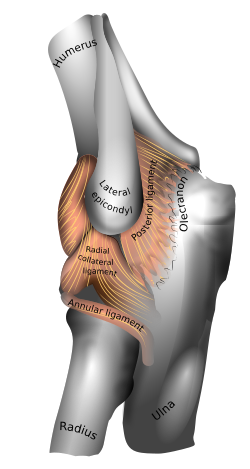
Elbow joint anatomy. Ligaments of the elbow joint. The ends of the bones are covered with cartilage. Elbow joint allows flexion and extension.
Biceps brachii is the main elbow flexor but as a biarticular. It is a synovial joint structurally but functionally is a hinge joint. The elbow is a hinged joint made up of three bones the humerus ulna and radius.
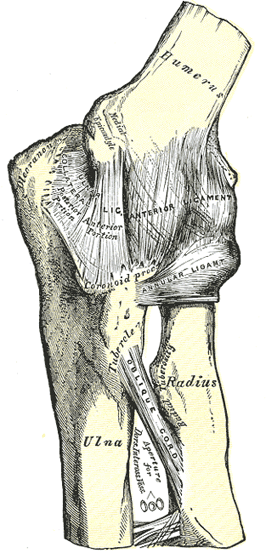
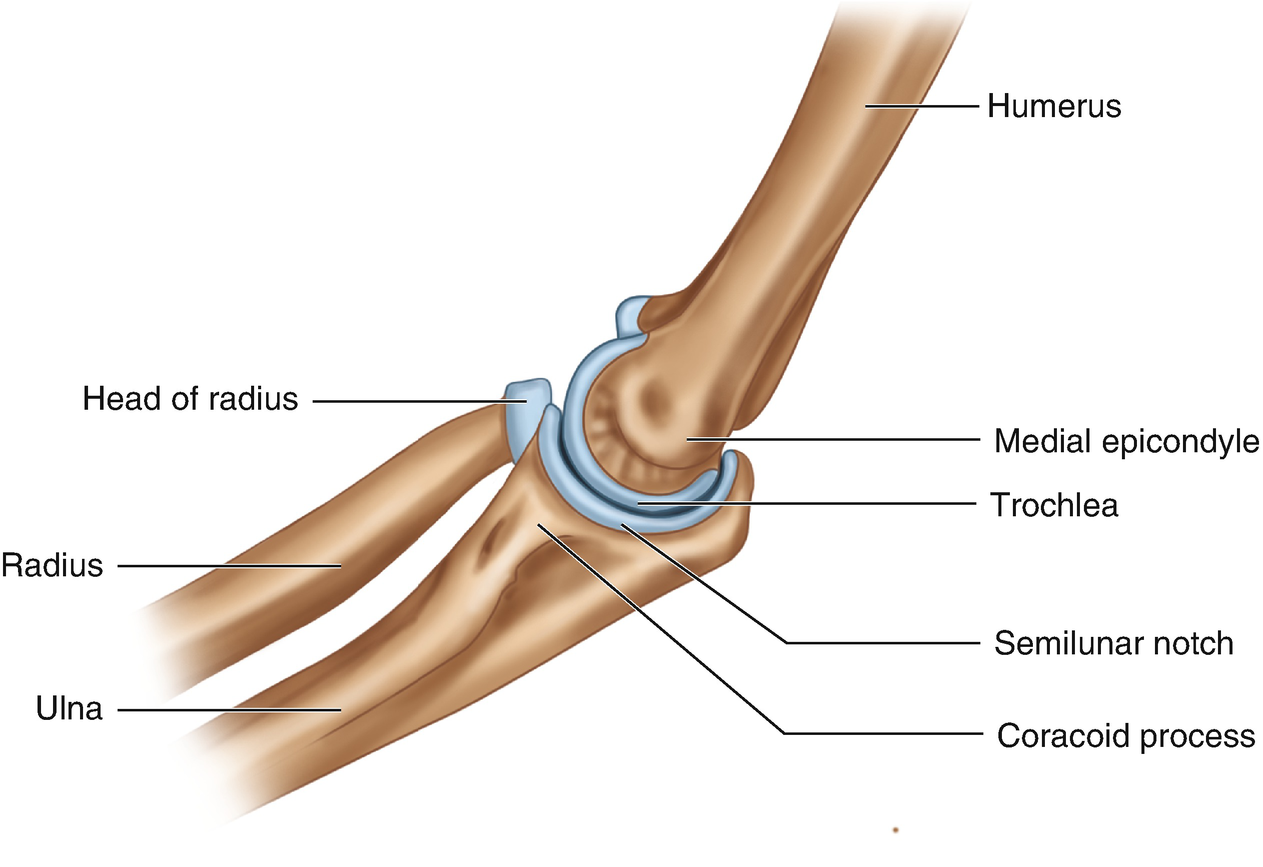
The elbow joint is made up of three bones the humerus ulna and radius. The unique positioning and interaction of the bones in the joint allows for a small amount of rotation as well as hinge action. Blood supply and innervation.
The elbow joint has a synovial membranelined joint capsule that is contiguous between the hinge and radioulnar aspects of the joint. The synovial lining covers the internal surface of the fibrous joint capsule and the nonarticular surfaces of the joint that are located intracapsularly. There are three main flexor muscles at the elbow.
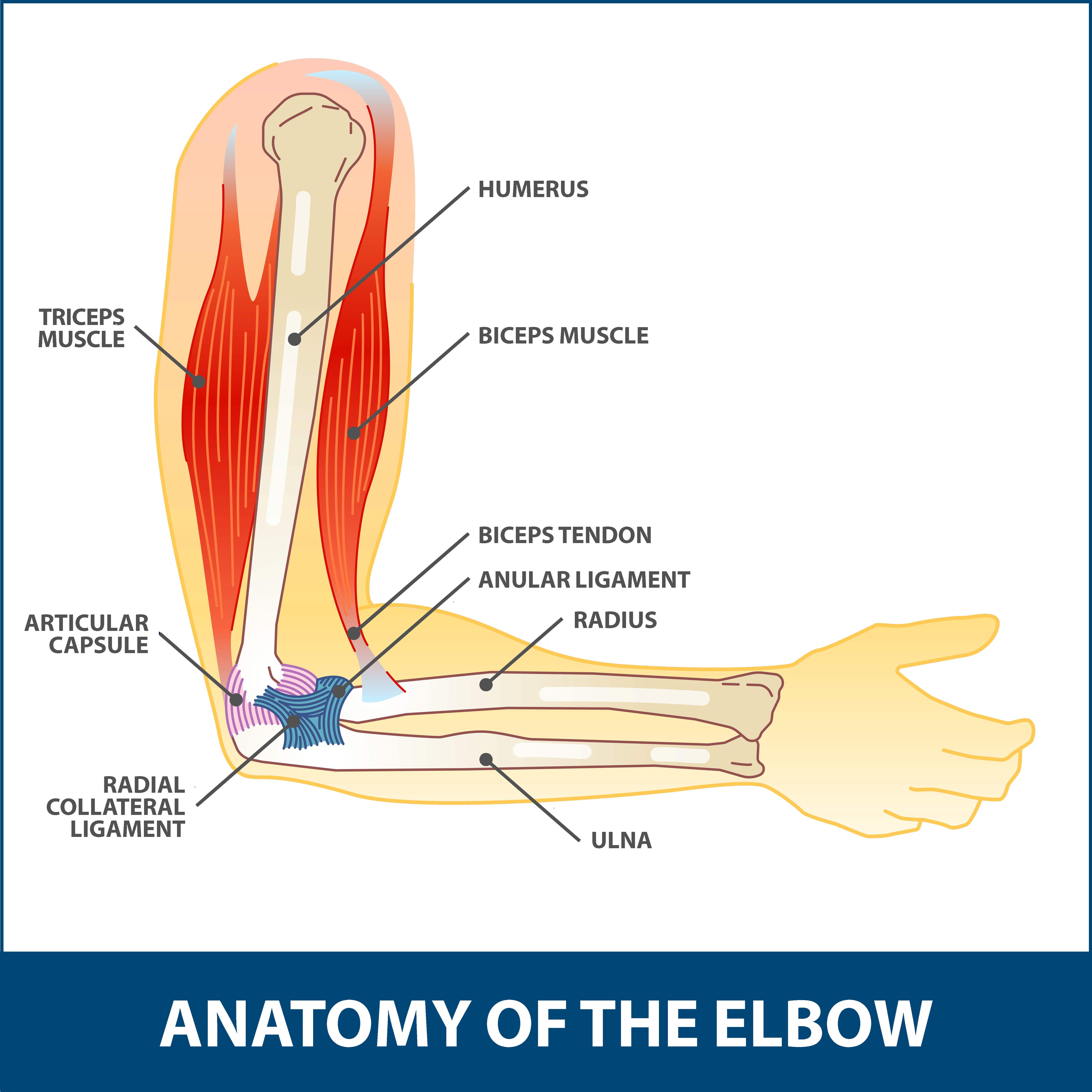
The anatomy of the elbow. The elbow allows the bending and extension of the forearm and it also allows the rotational movements of the radius and ulna that enable the palm of the hand to be turned upward or downward. The elbow is a hinge joint made up of the humerus ulna and radius.
Flexion brachialis biceps brachii brachioradialis. Anatomy of the elbow. The elbow joint is a complex hinge joint formed between the distal end of the humerus in the upper arm and the proximal ends of the ulna and radius in the forearm.
The elbow is one of the largest joints in the body. Extension triceps brachii and anconeus. The bones are held together with ligaments that form the joint capsule.
Brachioradialis acts essentially as an elbow flexor but also supinates during extreme pronation. There are a collection of ligaments that connect the bones forming. Cartilage has a rubbery consistency that allows the joints to slide easily against one another and absorb shock.
Humeroulnar joint is the joint between the trochlea on the medial aspect. The blood supply to the elbow joint is derived from a number. In conjunction with the shoulder joint and wrist the elbow gives the arm much of its versatility as well as structure and durability.
Elbow in human anatomy hinge joint formed by the meeting of the humerus bone of the upper arm and the radius and ulna bones of the forearm. Elbow joint connects the proper arm to the forearm. Brachialis acts exclusively as an elbow flexor and is one of the few muscles in.
 Anatomy Musculoskeletal Ultrasonography
Anatomy Musculoskeletal Ultrasonography
Gale Academic Onefile Document The Elbow Joint Anatomy
Anatomy Of The Elbow Joint Posterior Elbow View And
 Elbow Joint Anatomy Movement Muscle Involvement Elbow
Elbow Joint Anatomy Movement Muscle Involvement Elbow
 Arthroscopic Debridement Elbow Florida Orthopaedic Institute
Arthroscopic Debridement Elbow Florida Orthopaedic Institute
 Canine Dog Elbow Joint Anatomy Anatomical Model 9070
Canine Dog Elbow Joint Anatomy Anatomical Model 9070
Anatomy Of The Elbow Joint Posterior Elbow View And
 Elbow Anatomy Elbow Pain Chicago Westchester Hinsdale Il
Elbow Anatomy Elbow Pain Chicago Westchester Hinsdale Il
2 06 Anterior Posterior Forearm Elbow Joint Anatomy
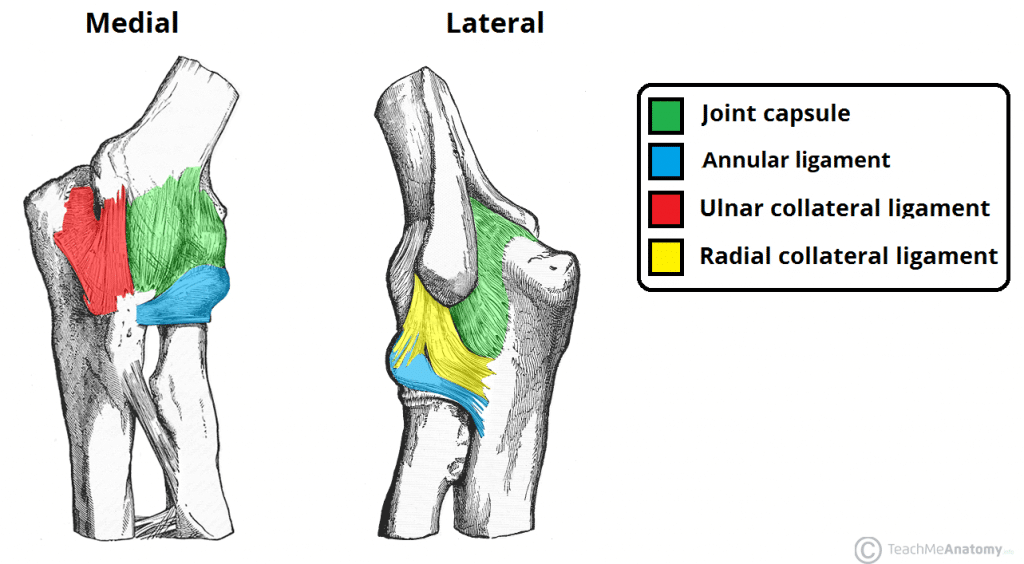 The Elbow Joint Structure Movement Teachmeanatomy
The Elbow Joint Structure Movement Teachmeanatomy
 Acc Shoulder And Elbow Anatomical Chart
Acc Shoulder And Elbow Anatomical Chart
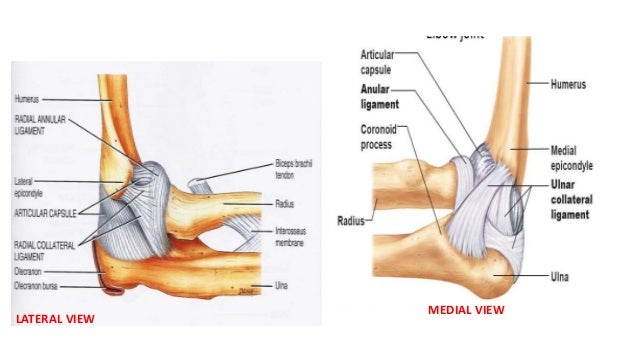 Elbow Joint Anatomy And Examination
Elbow Joint Anatomy And Examination
Elbow Anatomy Online Biology Dictionary
Elbow Anatomy Orthopedic Surgery Algonquin Il
 Elbow Joint Anatomy Watercolor Print Anatomy Art Humerus Ulna Radius Watercolor Orthopedic Art
Elbow Joint Anatomy Watercolor Print Anatomy Art Humerus Ulna Radius Watercolor Orthopedic Art
 File Human Arm Bones Diagram Svg Wikipedia
File Human Arm Bones Diagram Svg Wikipedia
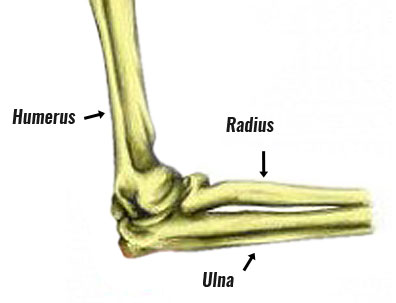 Elbow Muscles Sportsinjuryclinic Net Origin Insertion And
Elbow Muscles Sportsinjuryclinic Net Origin Insertion And
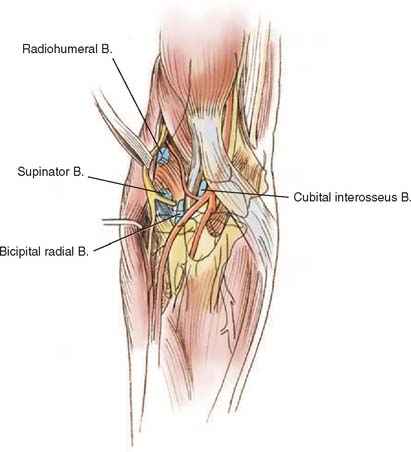 Anatomy Of The Elbow Joint Clinical Gate
Anatomy Of The Elbow Joint Clinical Gate
 The Elbow Joint And Forearm Yogabody Anatomy Kinesiology
The Elbow Joint And Forearm Yogabody Anatomy Kinesiology
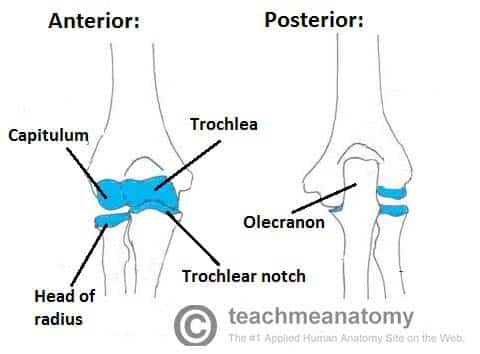 The Elbow Joint Structure Movement Teachmeanatomy
The Elbow Joint Structure Movement Teachmeanatomy
 Human Anatomy Quizzes Elbow Joint Bursa Wikiversity
Human Anatomy Quizzes Elbow Joint Bursa Wikiversity



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Elbow Joint Anatomy"
Posting Komentar