Anatomy Of A Hernia
The hiatus is an opening in the diaphragm the muscular wall separating the chest cavity from the. Although the clinical anatomy of the inguinal region has traditionally been a focus for hernia surgeons increasing attention is now applied to abdominal wall clinical anatomy for abdominal wall reconstruction.
Clinical Anatomy Of The Abdominal Wall Hernia Surgery Oa
The 2 types of inguinal.
Anatomy of a hernia. It can be fat bowel or in some cases the genitourinary tract. A is the normal anatomy b is a pre stage c is a sliding hiatal hernia and d is a paraesophageal rolling type. A type i hernia is also known as a sliding hiatal hernia.
Four types of esophageal hiatal hernia are identified. Hernia anatomy the layers of the abdominal wall the first concept to understand is the basic layers of the abdominal wall. Its function amongst other things is to hold in the abdominal contents principally the intestines.
Any time an internal body part pushes into an area where it doesnt belong its called a hernia. These layers are a bit different between the umbilical region and the groin but overall the basic layers are the same. A hernia occurs when an organ or fatty tissue squeezes through a weak spot in a surrounding muscle or connective tissue called fascia.
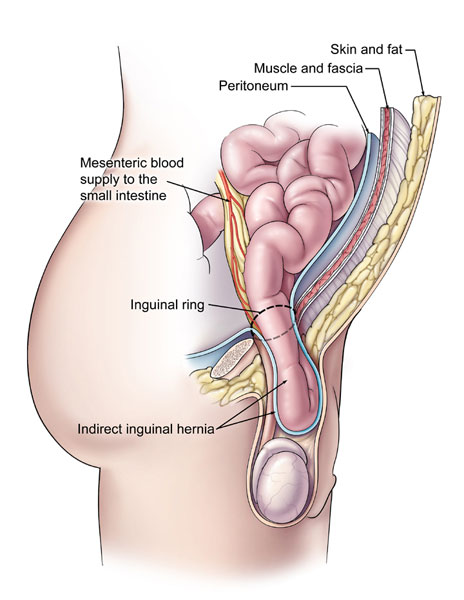
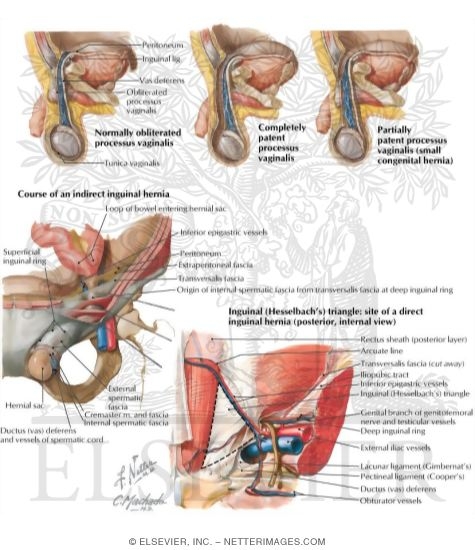
It is deep set in the body causing extra challenges in treatment options and is one of the most commonly misdiagnosed conditions. Indirect where the peritoneal sac enters the inguinal canal through the deep inguinal ring. The most common location for hernia is the abdomen.
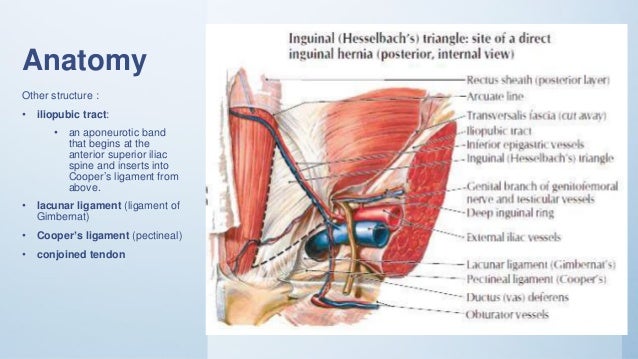
In lumbar hernia anatomy this is the section that can herniate collapse and sometimes obstruct the bowels. Hernias involving the inguinal canal can be divided into two main categories. During a laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair the dangerous triangle the triangle of doom refers to a triangular area bound by the vas deferens the testicular vessels and the peritoneal fold.
Within the boundaries of this area you can find the external iliac artery and vein. The abdominal wall a sheet of tough muscle and tendon that runs down from the ribs to the legs at the groins acts as the bodys corset. An inguinal hernia is the protrusion of intra abdominal contents through a defect in the abdominal wall.
The surgeons understanding of the anatomy of the anterior abdominal wall is critical for successful hernia repair. The most common types of hernia are inguinal inner groin incisional resulting from an incision femoral outer groin umbilical belly button and hiatal upper stomach. The rarity of a ruptured hernia compounds the diagnosis problem and increases morbidity rates.
A hernia is defined as the protrusion of an organ or fascia through the wall of a cavity that normally contains it.
 Department Of Surgery Inguinal Hernia
Department Of Surgery Inguinal Hernia
 Direct Inguinal Hernias General Surgery Surgical Nursing
Direct Inguinal Hernias General Surgery Surgical Nursing
 Types Of Hernias The Hernia Clinic
Types Of Hernias The Hernia Clinic
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/8025/The_Hernia.png) Inguinal Canal Anatomy Contents And Hernias Kenhub
Inguinal Canal Anatomy Contents And Hernias Kenhub
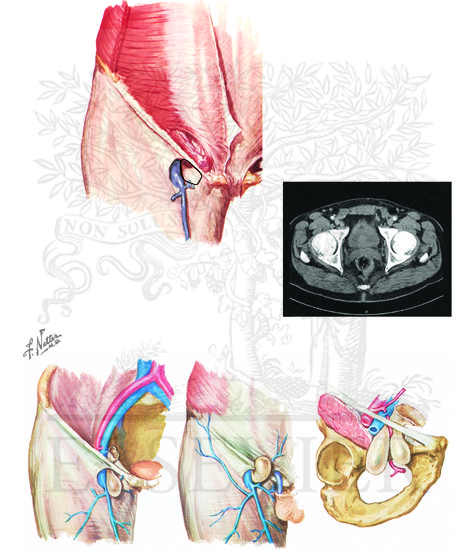 Femoral Hernia Anatomy Of Femoral Hernia
Femoral Hernia Anatomy Of Femoral Hernia
 14 Inguinal Hernia Target Anatomy Left Titles Incision
14 Inguinal Hernia Target Anatomy Left Titles Incision
 Inguinal Hernia Anatomy Faculty Of Medicine
Inguinal Hernia Anatomy Faculty Of Medicine
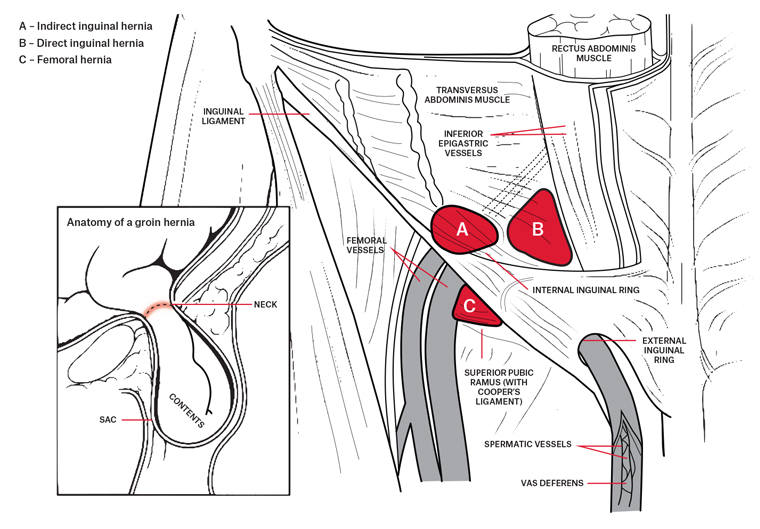 Racgp General Practitioner Primer On Groin Hernias
Racgp General Practitioner Primer On Groin Hernias
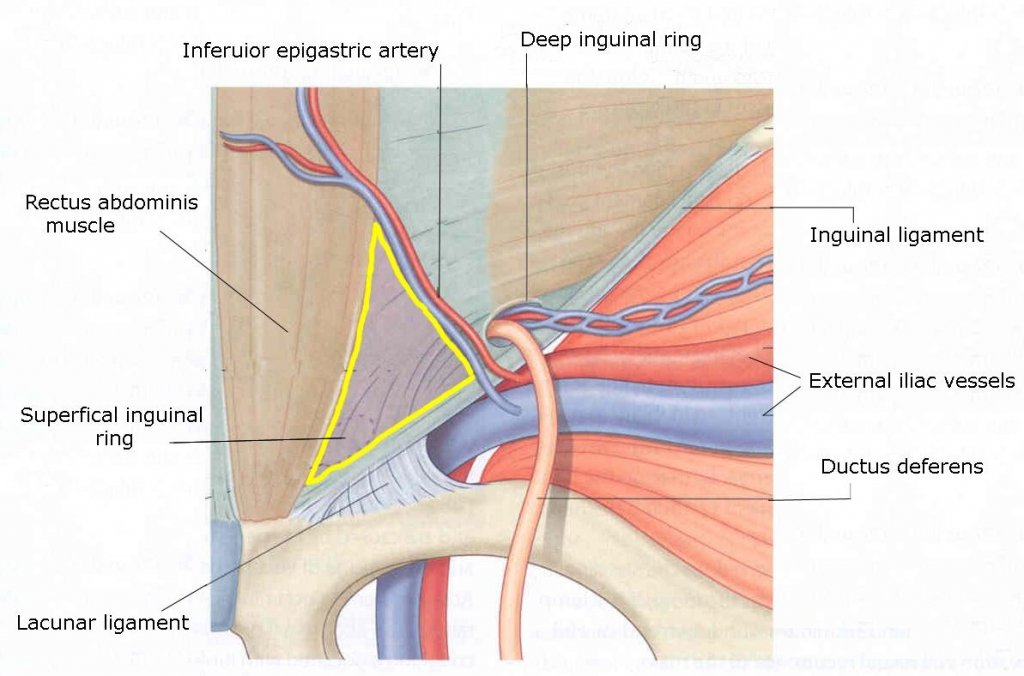
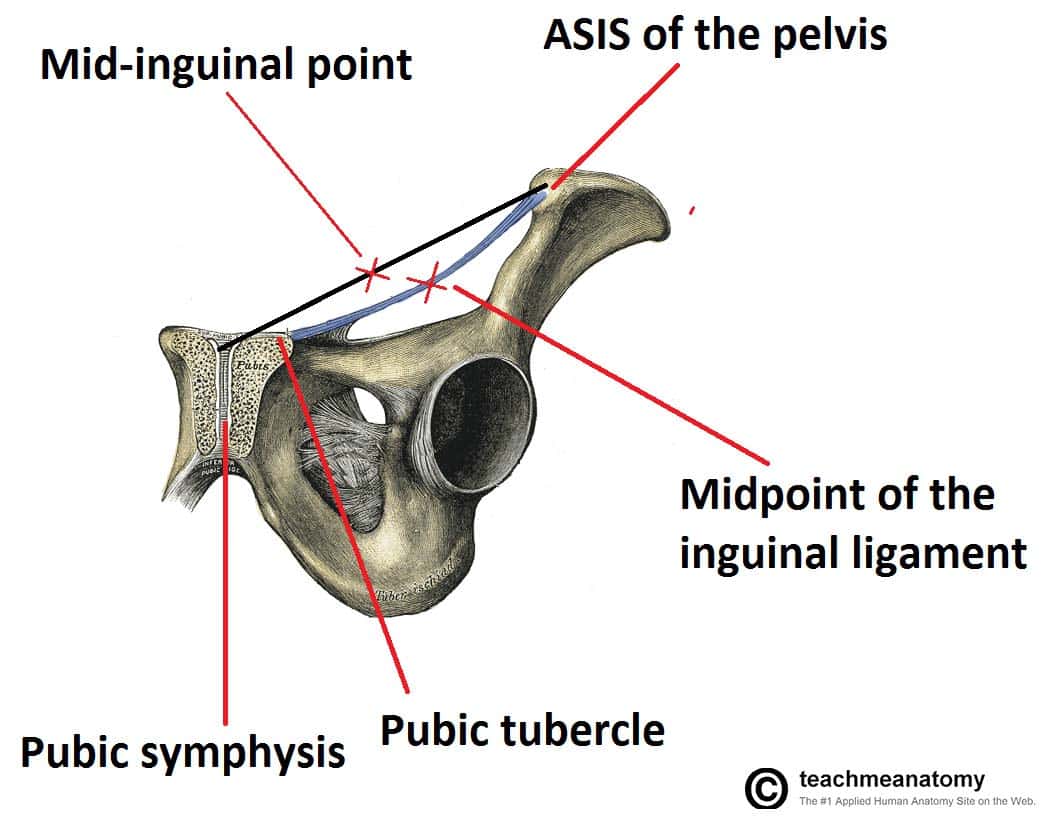 The Inguinal Canal Boundaries Contents Teachmeanatomy
The Inguinal Canal Boundaries Contents Teachmeanatomy
 The Anatomy Of Hernia The British Hernia Centre
The Anatomy Of Hernia The British Hernia Centre
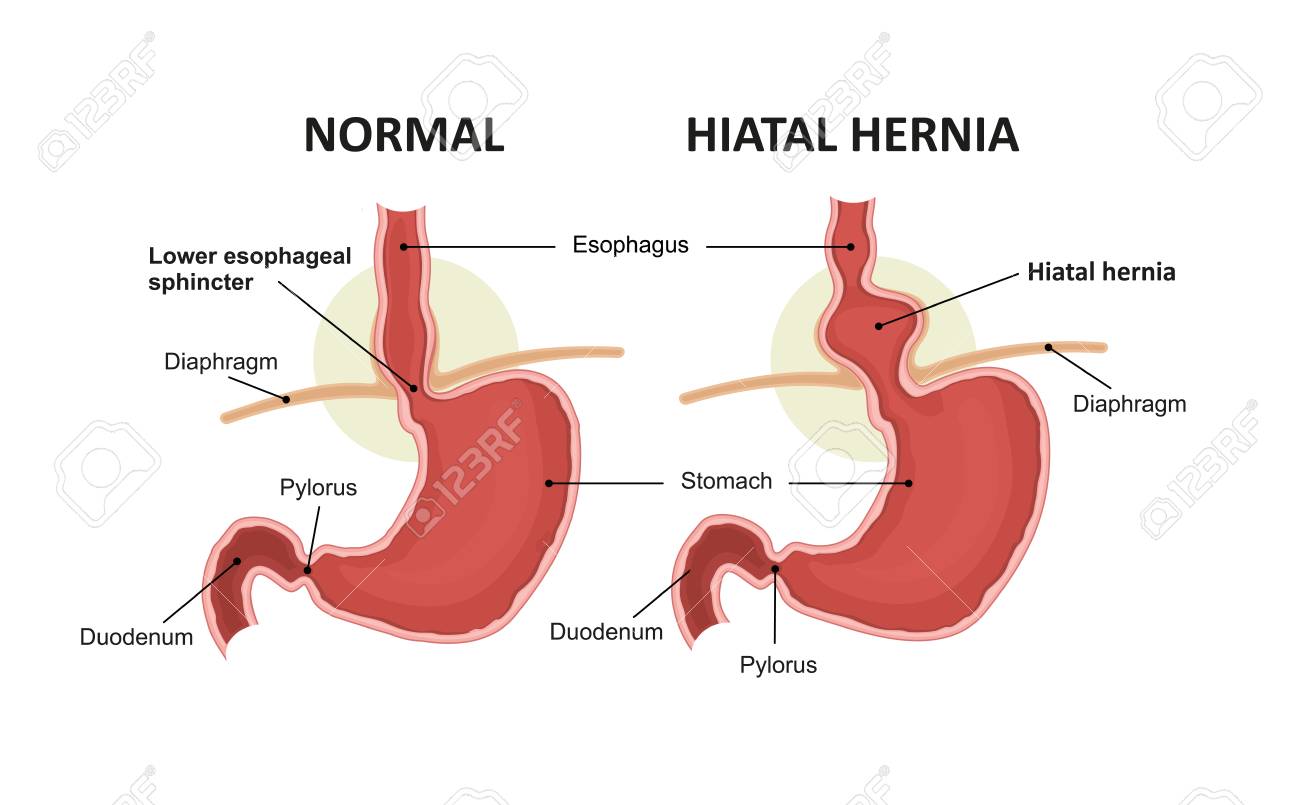
 Hiatal Hernia And Normal Anatomy Of The Stomach
Hiatal Hernia And Normal Anatomy Of The Stomach
 Surgical Anatomy Of Inguinal Hernia
Surgical Anatomy Of Inguinal Hernia
Anatomy Essentials For Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair
Clinical Anatomy Of The Abdominal Wall Hernia Surgery Oa
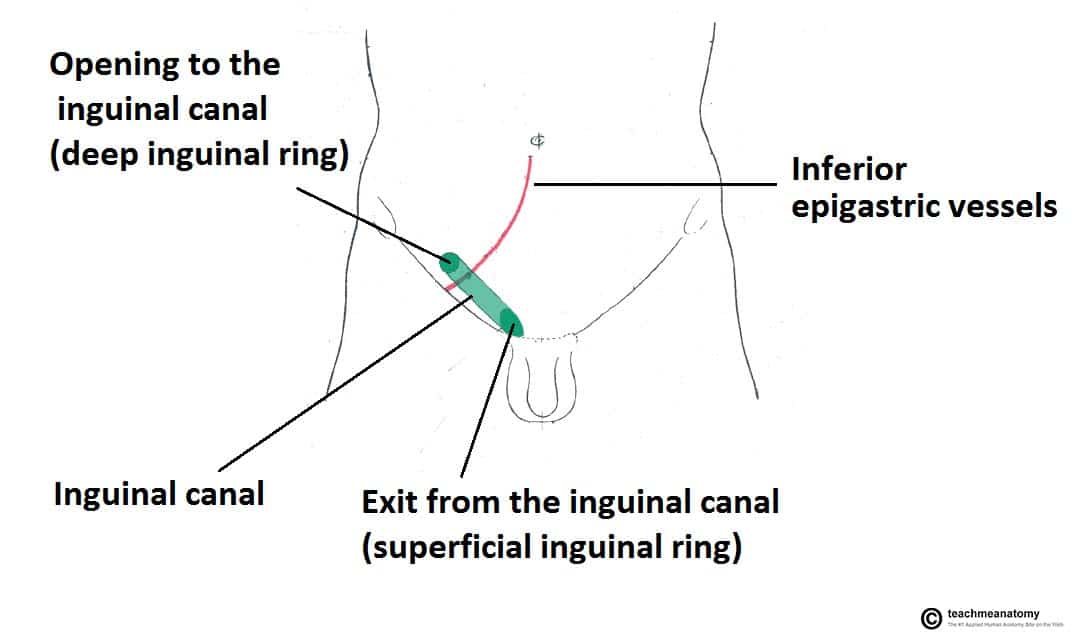 The Inguinal Canal Boundaries Contents Teachmeanatomy
The Inguinal Canal Boundaries Contents Teachmeanatomy
 Abdominal Wall Hernia An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Abdominal Wall Hernia An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
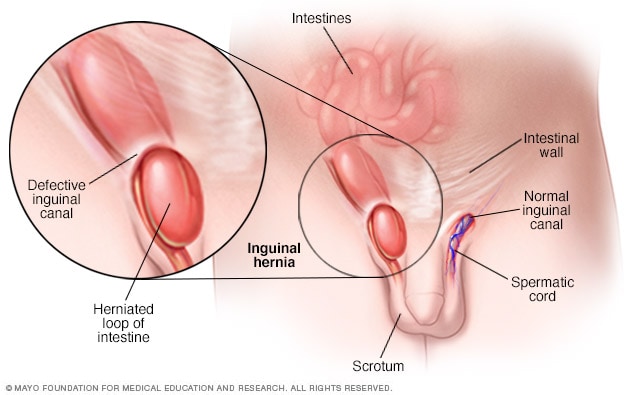 Inguinal Hernia Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
Inguinal Hernia Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
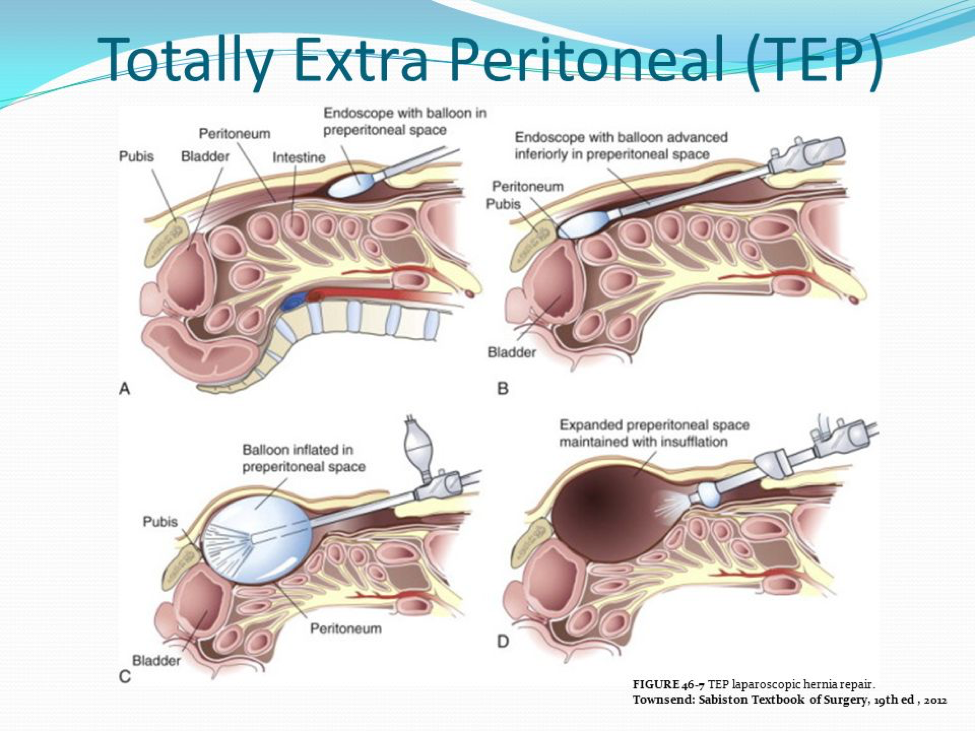
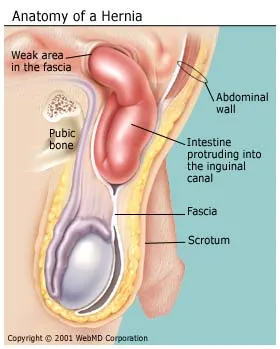 What Is A Hernia Inguinal Incisional Umbilical Hiatal
What Is A Hernia Inguinal Incisional Umbilical Hiatal
Inguinal Hernia Cleveland Clinic
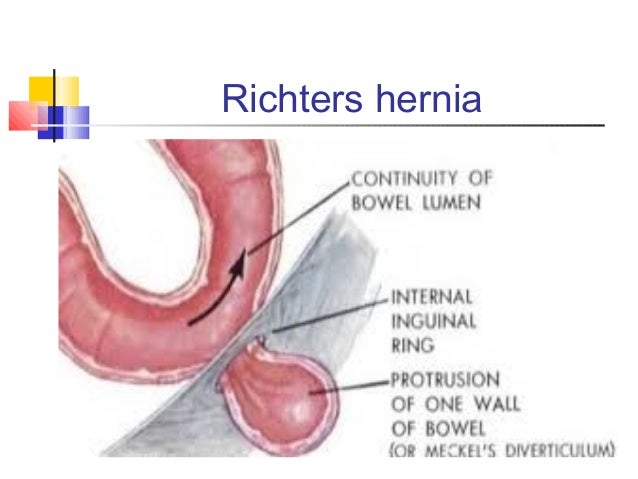 Surgical Anatomy Inguinal Canal Dr Mnr
Surgical Anatomy Inguinal Canal Dr Mnr


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of A Hernia"
Posting Komentar